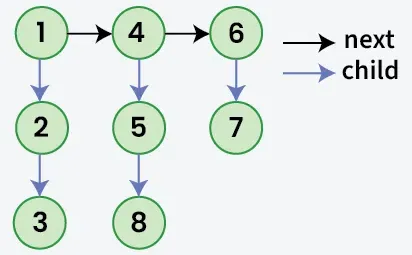
Annettu linkitetty luettelo, jossa lisäksi seuraavaksi osoitin jokaisessa solmussa on a lapsi osoitin, joka voi osoittaa tai olla osoittamatta erilliseen luetteloon. Näissä lapsiluetteloissa voi olla yksi tai useampi omia lapsiaan tuottamaan a monitasoinen linkitetty lista. Koska pää -lta ensimmäinen taso luettelosta. Tehtävänä on litistää luettelo niin, että kaikki solmut näkyvät kohdassa a yksitasoinen linkitetty lista. Tasoita luettelo siten, että kaikki solmut ensimmäinen taso pitäisi tulla ensimmäinen sitten solmut toinen taso ja niin edelleen.
Esimerkkejä:
Syöte:
Lähtö: 1->4->6->2->5->7->3->8
Selitys: Monitasoinen linkitetty luettelo on litistetty, koska siinä ei ole alaosoittimia.
Olemme keskustelleet monitasoisen linkitetyn luettelon litistäminen jossa solmuissa on kaksi osoitinta alas ja seuraavaksi. Edellisessä postauksessa me litistetty linkitetty lista tasoltaan. Kuinka litistää linkitetty luettelo, kun meidän on aina käsiteltävä osoitin alaspäin ennen seuraavaa jokaisessa solmussa.
Sisällysluettelo
- [Odotettu lähestymistapa] Rekursion käyttö - O(n) aika ja O(n) avaruus
- [Vaihtoehtoinen lähestymistapa] Pinon käyttäminen - O(n) aika ja O(n) tila
[Odotettu lähestymistapa] Rekursion käyttö - O(n) aika ja O(n) avaruus
C++Lähestymistapa on rekursiivisesti litistää a monitasoinen linkitetty lista kulkemalla kunkin solmun ja sen alisolmujen läpi. Ensimmäinen litistää lapsiluetteloa käyttämällä rekursiota. Kun lapsiluettelo on litistetty, siirry kohtaan seuraava solmu järjestyksessä. Säilytä ajon aikana a viite kohtaan aiemmin vieraillut solmu ja linkitä se nykyiseen solmuun. Tämä prosessi varmistaa, että kaikki eri tasojen solmut on yhdistetty a yksi lineaarinen luettelo säilyttäen samalla syvyyskohtainen järjestys.
// A C++ program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise #include
// A Java program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise class Node { int data; Node next down; Node(int x) { data = x; next = down = null; } } class GfG { static void flattenList(Node curr Node[] prev) { if (curr == null) return; // Add the current element to the list. if (prev[0] != null) prev[0].next = curr; prev[0] = curr; // Store the next pointer Node next = curr.next; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList(curr.down prev); // Recursively add the next list flattenList(next prev); } static void printList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { System.out.print(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); Node[] prev = new Node[1]; flattenList(head prev); printList(head); } }
# A Python program to flatten a multi- # linked list depth-wise class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.next = None self.down = None def flatten_list(curr prev): if curr is None: return # Add the current element to the list. if prev[0] is not None: prev[0].next = curr prev[0] = curr # Store the next pointer next_node = curr.next # Recursively add the bottom list flatten_list(curr.down prev) # Recursively add the next list flatten_list(next_node prev) def print_list(head): curr = head while curr is not None: print(curr.data end=' ') curr = curr.next print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Create a hard coded multi-linked list. # 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 # | | # 7 22 # | | # 8 50 # | # 30 head = Node(5) head.down = Node(7) head.down.down = Node(8) head.down.down.down = Node(30) head.next = Node(10) head.next.next = Node(19) head.next.next.down = Node(22) head.next.next.down.down = Node(50) head.next.next.next = Node(28) prev = [None] flatten_list(head prev) print_list(head)
// A C# program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using System; class Node { public int data; public Node next down; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = down = null; } } class GfG { static void FlattenList(Node curr ref Node prev) { if (curr == null) return; // Add the current element to the list. if (prev != null) prev.next = curr; prev = curr; // Store the next pointer Node next = curr.next; // Recursively add the bottom list FlattenList(curr.down ref prev); // Recursively add the next list FlattenList(next ref prev); } static void PrintList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { Console.Write(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main(string[] args) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); Node prev = null; FlattenList(head ref prev); PrintList(head); } }
// A Javascript program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.next = null; this.down = null; } } function flattenList(curr prev) { if (curr === null) return; // Add the current element to the list. if (prev[0] !== null) prev[0].next = curr; prev[0] = curr; // Store the next pointer let next = curr.next; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList(curr.down prev); // Recursively add the next list flattenList(next prev); } function printList(head) { let curr = head; while (curr !== null) { console.log(curr.data); curr = curr.next; } } // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 let head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); let prev = [null]; flattenList(head prev); printList(head);
Lähtö
5 7 8 30 10 19 22 50 28
[Vaihtoehtoinen lähestymistapa] Pinon käyttäminen - O(n) aika ja O(n) tila
C++Lähestymistapa on kulkea läpi monitasoinen linkitetty luettelo käyttämällä a pino . Aloita työntämällä the pääsolmu pinoon. Sitten kun pino ei ole tyhjä pop yläsolmu ja käsittele se. Jokaiselle solmulle Työnnä sen seuraava ja alas osoittimet (jos niitä on) pinoon. Tämän prosessin aikana linkitä nykyinen solmu edelliseen solmuun luettelon säilyttäminen litistetyssä muodossa. Läpikulku varmistaa, että solmut kaikilta tasoilta on yhdistetty a yksitasoinen linkitetty luettelo syvyysjärjestyksen säilyttäminen.
// A C++ program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack #include
// A Java program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack import java.util.Stack; class Node { int data; Node next down; Node(int x) { data = x; next = down = null; } } class GfG { static void flattenList(Node head) { if (head == null) return; Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>(); stack.push(head); Node prev = null; while (!stack.isEmpty()) { Node curr = stack.pop(); // Push the next node first if (curr.next != null) stack.push(curr.next); // Push the bottom node into stack if (curr.down != null) stack.push(curr.down); // Add the current element to the list if (prev != null) prev.next = curr; prev = curr; } } static void printList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { System.out.print(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); flattenList(head); printList(head); } }
# A Python program to flatten a multi- # linked list depth-wise using stack class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.next = None self.down = None def flatten_list(head): if head is None: return stack = [head] prev = None while stack: curr = stack.pop() # Push the next node first if curr.next: stack.append(curr.next) # Push the bottom node into stack if curr.down: stack.append(curr.down) # Add the current element to the list if prev: prev.next = curr prev = curr def print_list(head): curr = head while curr: print(curr.data end=' ') curr = curr.next print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Create a hard coded multi-linked list. # 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 # | | # 7 22 # | | # 8 50 # | # 30 head = Node(5) head.down = Node(7) head.down.down = Node(8) head.down.down.down = Node(30) head.next = Node(10) head.next.next = Node(19) head.next.next.down = Node(22) head.next.next.down.down = Node(50) head.next.next.next = Node(28) flatten_list(head) print_list(head)
// A C# program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node next down; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = down = null; } } class GfG { static void FlattenList(Node head) { if (head == null) return; Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); stack.Push(head); Node prev = null; while (stack.Count > 0) { Node curr = stack.Pop(); // Push the next node first if (curr.next != null) stack.Push(curr.next); // Push the bottom node into stack if (curr.down != null) stack.Push(curr.down); // Add the current element to the list if (prev != null) prev.next = curr; prev = curr; } } static void PrintList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { Console.Write(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main(string[] args) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); FlattenList(head); PrintList(head); } }
// A Javascript program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.next = null; this.down = null; } } function flattenList(head) { if (head === null) return; let stack = [head]; let prev = null; while (stack.length > 0) { let curr = stack.pop(); // Push the next node first if (curr.next !== null) stack.push(curr.next); // Push the bottom node into stack if (curr.down !== null) stack.push(curr.down); // Add the current element to the list if (prev !== null) prev.next = curr; prev = curr; } } function printList(head) { let curr = head; while (curr !== null) { console.log(curr.data); curr = curr.next; } } // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 let head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); flattenList(head); printList(head);
Lähtö
5 7 8 30 10 19 22 50 28