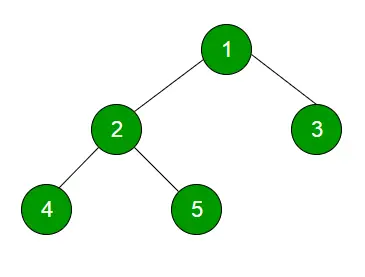
Tasojärjestyksen läpikäynti tekniikka määritellään menetelmäksi puun läpikulkuun siten, että kaikki samalla tasolla olevat solmut kulkevat kokonaan ennen seuraavan tason läpikulkua.
Esimerkki:
Suositeltu harjoitustason tilauksen läpikulku Kokeile sitä!Syöte:
Lähtö:
1
23
Neljä viisi
Kuinka tasotilausten läpikäynti toimii?
Tasojärjestyksen läpikulun pääideana on kulkea kaikki alemman tason solmut ennen siirtymistä mihinkään korkeamman tason solmuihin. Tämä voidaan tehdä jollakin seuraavista tavoista:
- naiivi (puun korkeuden etsiminen ja jokaisen tason poikki ja sen tason solmujen tulostaminen)
- käyttämällä jonoa tehokkaasti.
Tasojärjestyksen läpikäynti (naiivi lähestymistapa):
löytö korkeus puusta. Suorita sitten jokaiselle tasolle rekursiivinen funktio säilyttämällä nykyinen korkeus. Aina kun solmun taso vastaa, tulosta kyseinen solmu.
Alla on yllä olevan lähestymistavan toteutus:
C++ // Recursive CPP program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree #include using namespace std; // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child class node { public: int data; node *left, *right; }; // Function prototypes void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level); int height(node* node); node* newNode(int data); // Function to print level order traversal a tree void printLevelOrder(node* root) { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Print nodes at a current level void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) cout << root->tiedot<< ' '; else if (level>1) { printCurrentLevel(juuri->vasen, taso - 1); printCurrentLevel(juuri->oikea, taso - 1); } } // Laske puun 'korkeus' -- // solmujen lukumäärä pisintä polkua pitkin juurisolmusta // alas kaukaisimpaan lehtisolmuun. int korkeus(solmu* solmu) { if (solmu == NULL) return 0; else { // Laske jokaisen alipuun korkeus int lheight = korkeus(solmu->vasen); int rheight = korkeus(solmu->oikea); // Käytä suurempaa if (lheight> rheight) { return (lheight + 1); } else { return (oikea + 1); } } } // Aputoiminto, joka varaa // uuden solmun annetuilla tiedoilla ja // NULL vasen ja oikea osoittimia. solmu* uusiSolmu(int data) { solmu* Solmu = uusi solmu(); Solmu->tiedot = data; Solmu->vasen = NULL; Solmu->oikea = NULL; paluu (solmu); } // Ohjainkoodi int main() { solmu* root = newNode(1); juuri->vasen = uusiSolmu(2); root->right = newNode(3); juuri->vasen->vasen = uusiSolmu(4); juuri->vasen->oikea = uusiSolmu(5); cout<< 'Level Order traversal of binary tree is
'; printLevelOrder(root); return 0; } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra> C // Recursive C program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree #include #include // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child struct node { int data; struct node *left, *right; }; // Function prototypes void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level); int height(struct node* node); struct node* newNode(int data); // Function to print level order traversal a tree void printLevelOrder(struct node* root) { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Print nodes at a current level void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) printf('%d ', root->tiedot); else if (taso> 1) { printCurrentLevel(juuri->vasen, taso - 1); printCurrentLevel(juuri->oikea, taso - 1); } } // Laske puun 'korkeus' -- solmujen lukumäärä pisimmällä polulla juurisolmusta // alas kaukaisimpaan lehtisolmuun int korkeus(rakenne solmu* solmu) { if (solmu == NULL) palauttaa 0; else { // Laske jokaisen alipuun korkeus int lheight = korkeus(solmu->vasen); int rheight = korkeus(solmu->oikea); // Käytä suurempaa if (lheight> rheight) return (lheight + 1); muuten paluu (oikea + 1); } } // Aputoiminto, joka varaa uuden solmun // annetuilla tiedoilla ja NULL vasemmalla ja oikealla osoittimilla. struct solmu* uusiSolmu(int data) { struct solmu* solmu = (rakennesolmu*)malloc(koko(rakennesolmu)); solmu->tiedot = data; solmu->vasen = NULL; solmu->oikea = NULL; paluu (solmu); } // Ohjainohjelma yllä olevien funktioiden testaamiseen int main() { struct node* root = newNode(1); juuri->vasen = uusiSolmu(2); root->right = newNode(3); juuri->vasen->vasen = uusiSolmu(4); juuri->vasen->oikea = uusiSolmu(5); printf('Binaaripuun tasojärjestyksen läpikulku on
'); printLevelOrder(juuri); paluu 0; }> Java // Recursive Java program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree // Class containing left and right child of current // node and key value class Node { int data; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class BinaryTree { // Root of the Binary Tree Node root; public BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Function to print level order traversal of tree void printLevelOrder() { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- the number of // nodes along the longest path from the root node // down to the farthest leaf node. int height(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; else { // Compute height of each subtree int lheight = height(root.left); int rheight = height(root.right); // use the larger one if (lheight>oikea) paluu (lheight + 1); muuten paluu (oikea + 1); } } // Tulosta solmut nykyisellä tasolla void printCurrentLevel(Solmun juuri, int taso) { if (root == null) return; if (taso == 1) System.out.print(root.data + ' '); else if (taso> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, level - 1); } } // Ohjainohjelma yllä olevien toimintojen testaamiseen public static void main(String args[]) { BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); puu.juuri = uusi solmu(1); puu.juuri.vasen = uusi solmu(2); puu.juuri.oikea = uusi solmu(3); tree.root.left.left = uusi solmu(4); puu.juuri.vasen.oikea = uusi solmu(5); System.out.println('Tasojärjestyksen läpikulku' + 'binääripuu on '); tree.printLevelOrder(); } }> Python # Recursive Python program for level # order traversal of Binary Tree # A node structure class Node: # A utility function to create a new node def __init__(self, key): self.data = key self.left = None self.right = None # Function to print level order traversal of tree def printLevelOrder(root): h = height(root) for i in range(1, h+1): printCurrentLevel(root, i) # Print nodes at a current level def printCurrentLevel(root, level): if root is None: return if level == 1: print(root.data, end=' ') elif level>1: printCurrentLevel(root.left, level-1) printCurrentLevel(juuri.oikea, taso-1) # Laske puun korkeus - solmujen määrä # pisintä polkua pitkin juurisolmusta alas # kauimpana lehteen solmu def korkeus(solmu): jos solmu on Ei mitään: palauta 0 else: # Laske kunkin alipuun korkeus lheight = korkeus(solmu.vasen) rheight = korkeus(solmu.oikea) # Käytä suurempaa, jos lheight> rheight: return lheight+1 else: return rheight+1 # Ohjainohjelma testaamaan yllä olevaa toimintoa, jos __name__ == '__main__': root = Solmu(1) root.left = Solmu(2) root.right = Solmu(3) root. left.left = Solmu(4) root.left.right = Solmu(5) print('Binääripuun tasojärjestys on -') printLevelOrder(root) # Tämän koodin on toimittanut Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)> C# // Recursive c# program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree using System; // Class containing left and right // child of current node and key value public class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class GFG { // Root of the Binary Tree public Node root; public void BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Function to print level order // traversal of tree public virtual void printLevelOrder() { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) { printCurrentLevel(root, i); } } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- // the number of nodes along the longest // path from the root node down to the // farthest leaf node. public virtual int height(Node root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } else { // Compute height of each subtree int lheight = height(root.left); int rheight = height(root.right); // use the larger one if (lheight>oikea) { paluu (lheight + 1); } else { return (oikea + 1); } } } // Tulosta solmut nykyisellä tasolla public virtual void printCurrentLevel(Solmun juuri, int taso) { if (root == null) { return; } if (taso == 1) { Console.Write(root.data + ' '); } else if (taso> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, level - 1); } } // Ohjainkoodi public static void Main(string[] args) { GFG-puu = new GFG(); puu.juuri = uusi solmu(1); puu.juuri.vasen = uusi solmu(2); puu.juuri.oikea = uusi solmu(3); tree.root.left.left = uusi solmu(4); puu.juuri.vasen.oikea = uusi solmu(5); Console.WriteLine('Tasojärjestyksen läpikulku ' + 'binääripuun on '); tree.printLevelOrder(); } } // Tämän koodin on toimittanut Shrikant13>>Javascriptoikea) paluu (lheight + 1); muuten paluu (oikea + 1); } } // Tulosta solmut nykyisellä tasolla function printCurrentLevel(root , level) { if (root == null) return; if (taso == 1) console.log(root.data + ' '); else if (taso> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, level - 1); } } // Ohjainohjelma yllä olevien funktioiden testaamiseen root = new Node(1); root.left = uusi solmu(2); root.right = uusi solmu(3); root.left.left = uusi solmu(4); root.left.right = uusi solmu(5); console.log('Binaaripuun tasojärjestys on '); printLevelOrder(); // Tämän koodin tarjoaa umadevi9616>>
Lähtö Level Order traversal of binary tree is 1 2 3 4 5>
Aika monimutkaisuus: O(N), missä N on vinopuun solmujen lukumäärä.
Aputila: O(1) Jos otetaan huomioon rekursiopino, käytetty tila on O(N).
r c-kielellä
Tasojärjestyksen läpikäynti käyttämällä Jonottaa
Meidän täytyy käydä alemman tason solmuissa ennen korkeamman tason solmuja, tämä idea on melko samanlainen kuin jonon idea. Työnnä alemman tason solmut jonossa. Kun missä tahansa solmussa käydään, poista kyseinen solmu jonosta ja työnnä kyseisen solmun lapsi jonoon.
Tämä varmistaa, että alemman tason solmussa käydään ennen korkeamman tason solmua.
Alla on yllä olevan lähestymistavan toteutus:
C++ // C++ program to print level order traversal #include using namespace std; // A Binary Tree Node struct Node { int data; struct Node *left, *right; }; // Iterative method to find height of Binary Tree void printLevelOrder(Node* root) { // Base Case if (root == NULL) return; // Create an empty queue for level order traversal queueq; // Lisää jonoon juuri ja alusta korkeus q.push(root); while (q.empty() == false) { // Tulosta jonon etuosa ja poista se jonosta Node* node = q.front(); cout<< node->tiedot<< ' '; q.pop(); // Enqueue left child if (node->vasen != NULL) q.push(solmu->vasen); // Jonoa oikea lapsi if (solmu->oikea != NULL) q.push(solmu->oikea); } } // Aputoiminto uuden puusolmun luomiseen Node* newNode(int data) { Node* temp = new Node; temp->data = data; temp->vasen = temp->oikea = NULL; paluulämpötila; } // Ohjainohjelma yllä olevien funktioiden testaamiseen int main() { // Luodaan binääripuu, joka näkyy yllä olevassa kaaviossa Node* root = newNode(1); juuri->vasen = uusiSolmu(2); root->right = newNode(3); juuri->vasen->vasen = uusiSolmu(4); juuri->vasen->oikea = uusiSolmu(5); cout<< 'Level Order traversal of binary tree is
'; printLevelOrder(root); return 0; }> C // Iterative Queue based C program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree #include #include #define MAX_Q_SIZE 500 // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child struct node { int data; struct node* left; struct node* right; }; // Function prototypes struct node** createQueue(int*, int*); void enQueue(struct node**, int*, struct node*); struct node* deQueue(struct node**, int*); // Given a binary tree, print its nodes in level order // using array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder(struct node* root) { int rear, front; struct node** queue = createQueue(&front, &rear); struct node* temp_node = root; while (temp_node) { printf('%d ', temp_node->tiedot); // Jonoa vasen lapsi if (temp_node->left) enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->left); // Jonota oikea lapsi if (temp_node->right) enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->right); // Poista solmu jonosta ja tee siitä temp_node temp_node = deQueue(queue, &front); } } // Apufunktiot struct solmu** createQueue(int* front, int* rear) { struct solmu** queue = (struct node**)malloc( sizeof(struct node*) * MAX_Q_SIZE); *etu = *taka = 0; paluujono; } void enQueue(rakennesolmu** jono, int* takaosa, rakennesolmu* uusi_solmu) { jono[*taka] = uusi_solmu; (*takana)++; } struct node* deQueue(struct solmu** jono, int* etu) { (*etu)++; paluujono[*etu - 1]; } // Aputoiminto, joka varaa uuden solmun // annetuilla tiedoilla ja NULL vasemmalla ja oikealla osoittimilla. struct solmu* uusiSolmu(int data) { struct solmu* solmu = (rakennesolmu*)malloc(koko(rakennesolmu)); solmu->tiedot = data; solmu->vasen = NULL; solmu->oikea = NULL; paluu (solmu); } // Ohjainohjelma yllä olevien funktioiden testaamiseen int main() { struct node* root = newNode(1); juuri->vasen = uusiSolmu(2); root->right = newNode(3); juuri->vasen->vasen = uusiSolmu(4); juuri->vasen->oikea = uusiSolmu(5); printf('Binaaripuun tasojärjestyksen läpikulku on
'); printLevelOrder(juuri); paluu 0; }> Java // Iterative Queue based Java program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; // Class to represent Tree node class Node { int data; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = null; right = null; } } // Class to print Level Order Traversal class BinaryTree { Node root; // Given a binary tree. Print // its nodes in level order // using array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder() { Queuejono = uusi LinkedList(); queue.add(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // poll() poistaa nykyisen otsikon. Solmun tempSolmu = queue.poll(); System.out.print(tempNode.data + ' '); // Lisää jonoon vasen lapsi if (tempNode.left != null) { queue.add(tempNode.left); } // Jonota oikea lapsi if (tempNode.right != null) { queue.add(tempNode.right); } } } public static void main(String args[]) { // Binääripuun luominen ja // solmujen syöttäminen BinaryTree tree_level = new BinaryTree(); puu_taso.juuri = uusi solmu(1); tree_level.root.left = uusi solmu(2); tree_level.root.right = uusi solmu(3); tree_level.root.left.left = uusi solmu(4); tree_level.root.left.right = uusi solmu(5); System.out.println('Binaaripuun tasojärjestyksen läpikulku on - '); tree_level.printLevelOrder(); } }> Python # Python program to print level # order traversal using Queue # A node structure class Node: # A utility function to create a new node def __init__(self, key): self.data = key self.left = None self.right = None # Iterative Method to print the # height of a binary tree def printLevelOrder(root): # Base Case if root is None: return # Create an empty queue # for level order traversal queue = [] # Enqueue Root and initialize height queue.append(root) while(len(queue)>0): # Tulosta jonon etuosa ja # poista se jonosta print(queue[0].data, end=' ') node = queue.pop(0) # Jonon vasen lapsi, jos node.left ei ole Ei mitään: queue.append(node.left) # Jonota oikea lapsi, jos node.right ei ole Ei mitään: queue.append(node.right) # Ohjainohjelma yllä olevan toiminnon testaamiseksi, jos __name__ == '__main__': root = Node(1 ) root.left = Solmu(2) root.right = Solmu(3) root.left.left = Solmu(4) root.left.right = Solmu(5) print('Tasojärjestys Binaaripuun läpikulku on - ') printLevelOrder(root) # Tämän koodin on antanut Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)> C# // Iterative Queue based C# program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // Class to represent Tree node public class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = null; right = null; } } // Class to print Level Order Traversal public class BinaryTree { Node root; // Given a binary tree. Print // its nodes in level order using // array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder() { Queuejono = uusi jono(); jono.Enqueue(juuri); while (jono.Laskuri != 0) { Solmu tempSolmu = jono.Dequeue(); Console.Write(tempNode.data + ' '); // Jonoa vasen lapsi if (tempNode.left != null) { queue.Enqueue(tempNode.left); } // Jonota oikea lapsi if (tempNode.right != null) { queue.Enqueue(tempNode.right); } } } // Ohjainkoodi public static void Main() { // Binääripuun luominen ja // solmujen syöttäminen BinaryTree tree_level = new BinaryTree(); puu_taso.juuri = uusi solmu(1); tree_level.root.left = uusi solmu(2); tree_level.root.right = uusi solmu(3); tree_level.root.left.left = uusi solmu(4); tree_level.root.left.right = uusi solmu(5); Console.WriteLine('Binaaripuun tasojärjestyksen läpikulku ' + ' on - '); tree_level.printLevelOrder(); } } // Tämän koodin on toimittanut PrinciRaj1992>>Javascript Lähtö
Aputila: O(N) missä N on binääripuun solmujen lukumäärä.