Päätöksenteko on tärkein näkökohta lähes kaikissa ohjelmointikielissä. Kuten nimestä voi päätellä, päätöksenteon avulla voimme suorittaa tietyn koodilohkon tiettyä päätöstä varten. Täällä päätökset tehdään tiettyjen ehtojen pätevyydestä. Kuntotarkistus on päätöksenteon selkäranka.
ohjaaja Karan Johar
Pythonissa päätöksenteko suoritetaan seuraavilla lauseilla.
| lausunto | Kuvaus |
|---|---|
| Jos lausunto | If-lausetta käytetään tietyn ehdon testaamiseen. Jos ehto on tosi, koodilohko (jos-lohko) suoritetaan. |
| Jos - muuten Lausunto | If-else-käsky on samanlainen kuin if-lause, paitsi että se tarjoaa myös tarkistettavan ehdon väärän tapauksen koodilohkon. Jos if-lauseessa annettu ehto on epätosi, else-lause suoritetaan. |
| Sisäkkäinen if-lausunto | Sisäkkäisten if -lauseiden avulla voimme käyttää if ? else-lause ulomman if-lauseen sisällä. |
Sisennys Pythonissa
Ohjelmoinnin helpottamiseksi ja yksinkertaisuuden vuoksi python ei salli sulkeiden käyttöä lohkotason koodissa. Pythonissa sisennystä käytetään lohkon ilmoittamiseen. Jos kaksi lausetta ovat samalla sisennystasolla, ne ovat osa samaa lohkoa.
Yleensä neljä välilyöntiä annetaan lauseiden sisentämiseksi, jotka ovat tyypillinen sisennysmäärä pythonissa.
Sisennys on python-kielen eniten käytetty osa, koska se ilmoittaa koodilohkon. Kaikki yhden lohkon lauseet on tarkoitettu saman tason sisennykseen. Katsotaan, miten varsinainen sisennys tapahtuu päätöksenteossa ja muussa pythonissa.
Jos lause
If-lausetta käytetään tietyn ehdon testaamiseen, ja jos ehto on tosi, se suorittaa koodilohkon, joka tunnetaan nimellä if-block. If-lausekkeen ehto voi olla mikä tahansa kelvollinen looginen lauseke, joka voidaan joko arvioida tosi tai epätosi.
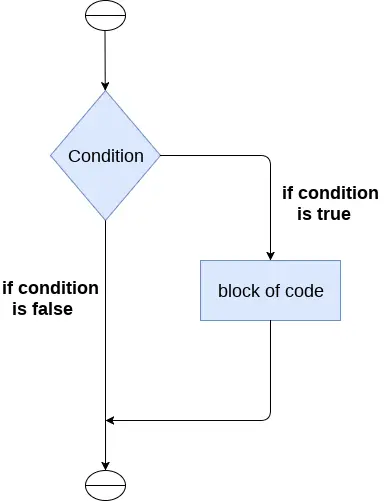
If-lauseen syntaksi on annettu alla.
muokkausnäppäimet
if expression: statement
Esimerkki 1
# Simple Python program to understand the if statement num = int(input('enter the number:')) # Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically if num%2 == 0: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The Given number is an even number')
Lähtö:
enter the number: 10 The Given number is an even number
Esimerkki 2: Ohjelma tulostaa suurimman kolmesta numerosta.
# Simple Python Program to print the largest of the three numbers. a = int (input('Enter a: ')); b = int (input('Enter b: ')); c = int (input('Enter c: ')); if a>b and a>c: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print ('From the above three numbers given a is largest'); if b>a and b>c: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print ('From the above three numbers given b is largest'); if c>a and c>b: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print ('From the above three numbers given c is largest');
Lähtö:
Enter a: 100 Enter b: 120 Enter c: 130 From the above three numbers given c is largest
Jos-else -lause
If-else-käsky tarjoaa else-lauseen yhdistettynä if-lauseeseen, joka suoritetaan ehdon väärässä tapauksessa.
Jos ehto on tosi, if-lohko suoritetaan. Muussa tapauksessa else-lohko suoritetaan.

If-else-käskyn syntaksi on annettu alla.
if condition: #block of statements else: #another block of statements (else-block)
Esimerkki 1: Ohjelma, jolla tarkistetaan, onko henkilö äänioikeutettu vai ei.
# Simple Python Program to check whether a person is eligible to vote or not. age = int (input('Enter your age: ')) # Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically if age>=18: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('You are eligible to vote !!'); else: print('Sorry! you have to wait !!');
Lähtö:
Enter your age: 90 You are eligible to vote !!
Esimerkki 2: Ohjelma tarkistaa, onko luku parillinen vai ei.
# Simple Python Program to check whether a number is even or not. num = int(input('enter the number:')) # Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically if num%2 == 0: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The Given number is an even number') else: print('The Given Number is an odd number')
Lähtö:
pawandeep rajan
enter the number: 10 The Given number is even number
Elif lausunto
Elif-käskyn avulla voimme tarkistaa useita ehtoja ja suorittaa tietyn lauseen lohkon niiden todellisen ehdon mukaan. Ohjelmassamme voi olla mikä tahansa määrä elif-lauseita tarpeidemme mukaan. Elifin käyttö on kuitenkin valinnaista.
Elif-lause toimii kuten if-else-if-ladder-lause C:ssä. Sen jälkeen tulee if-lause.
Elif-lauseen syntaksi on annettu alla.
if expression 1: # block of statements elif expression 2: # block of statements elif expression 3: # block of statements else: # block of statements

Esimerkki 1
# Simple Python program to understand elif statement number = int(input('Enter the number?')) # Here, we are taking an integer number and taking input dynamically if number==10: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The given number is equals to 10') elif number==50: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The given number is equal to 50'); elif number==100: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The given number is equal to 100'); else: print('The given number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100');
Lähtö:
Enter the number?15 The given number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100
Esimerkki 2
# Simple Python program to understand elif statement marks = int(input('Enter the marks? ')) # Here, we are taking an integer marks and taking input dynamically if marks > 85 and marks 60 and marks 40 and marks 30 and marks <= 40): # here, we are checking the condition. if condition is true, will enter block print('you scored grade c ...') else: print('sorry you fail ?') < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Enter the marks? 89 Congrats ! you scored grade A ... </pre> <hr></=> 