Koska a erityinen binääripuu jonka lehtien solmut ovat yhteydessä muotoon a pyöreä kaksoislinkitetty luettelo tehtävänä on löytää korkeus puusta.
Esimerkkejä:
suorita komentosarjan kuori
Syöte:

Lähtö: 2
Selitys: Binääripuun korkeus lehtisolmujen tunnistamisen jälkeen on 2. Yllä olevassa binääripuussa 6 5 ja 4 ovat lehtisolmuja ja ne muodostavat pyöreän kaksoislinkityksen. Tässä lehtisolmun vasen osoitin toimii pyöreän kaksoislinkitetyn listan edellisenä osoittimena ja sen oikea osoitin pyöreän kaksoislinkitetyn listan seuraavana osoittimena.Syöte:
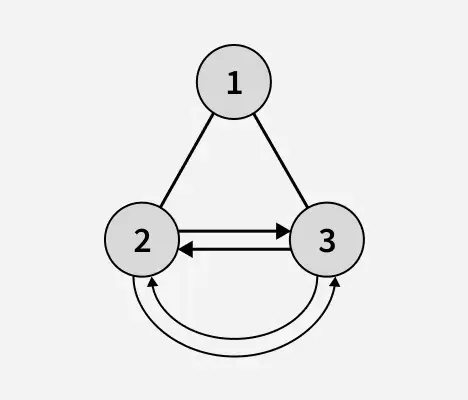
Lähtö: 1
Selitys: Binääripuun korkeus lehtisolmujen tunnistamisen jälkeen on 1. Yllä olevassa binääripuussa 2 ja 3 ovat lehtisolmuja ja ne muodostavat pyöreän kaksoislinkityksen.
Lähestyä :
matriisi c-kielellä
C++Ideana on seurata samanlainen lähestymistapa kuten teemme normaalin binääripuun korkeuden löytäminen . Me rekursiivisesti laskea korkeus / vasemmalle ja oikealle solmun alipuut ja määritä korkeus solmuun as max kahden lapsen pituuksista plus 1. Mutta vasen ja oikea lapsi a lehtien solmu ovat nolla normaaleille binääripuille. Mutta tässä lehtisolmu on pyöreä kaksoislinkitetty luettelosolmu. Joten jotta solmu olisi lehtisolmu, tarkistamme jos solmun vasen on oikea osoittaa solmu ja sen oikea on vasen osoittaa myös solmu itse.
// C++ program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list #include
// C program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list #include
// Java program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to check if given // node is a leaf node or node static boolean isLeaf(Node node) { // For a node to be a leaf node it should // satisfy the following two conditions: // 1. Node's left's right pointer should be // current node. // 2. Node's right's left pointer should be // current node. // If one condition is met it is guaranteed // that the other condition is also true. return node.left != null && node.left.right == node && node.right != null && node.right.left == node; } // Compute the height of a tree static int findTreeHeight(Node node) { // if node is NULL return -1. if (node == null) return -1; // if node is a leaf node return 0 if (isLeaf(node)) return 0; // compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + Math.max(findTreeHeight(node.left) findTreeHeight(node.right)); } public static void main(String[] args) { Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.left.left.left = new Node(6); // Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes Node l1 = root.left.left.left; Node l2 = root.left.right; Node l3 = root.right; // create circular doubly linked list out of // leaf nodes of the tree // set next pointer of linked list l1.right = l2; l2.right = l3; l3.right = l1; // set prev pointer of linked list l3.left = l2; l2.left = l1; l1.left = l3; System.out.println(findTreeHeight(root)); } }
# Python program to calculate height of a special tree # whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list class Node: def __init__(self data): self.data = data self.left = None self.right = None # function to check if given # node is a leaf node or node def isLeaf(node): # For a node to be a leaf node it should # satisfy the following two conditions: # 1. Node's left's right pointer should be # current node. # 2. Node's right's left pointer should be # current node. # If one condition is met it is guaranteed # that the other condition is also true. return (node.left and node.left.right == node and node.right and node.right.left == node) # Compute the height of a tree def findTreeHeight(node): # if node is NULL return -1. if node is None: return -1 # if node is a leaf node return 0 if isLeaf(node): return 0 # compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + max(findTreeHeight(node.left) findTreeHeight(node.right)) if __name__ == '__main__': root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) root.left.left.left = Node(6) # Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes l1 = root.left.left.left l2 = root.left.right l3 = root.right # create circular doubly linked list out of # leaf nodes of the tree # set next pointer of linked list l1.right = l2 l2.right = l3 l3.right = l1 # set prev pointer of linked list l3.left = l2 l2.left = l1 l1.left = l3 print(findTreeHeight(root))
// C# program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to check if given // node is a leaf node or node static bool isLeaf(Node node) { // For a node to be a leaf node it should // satisfy the following two conditions: // 1. Node's left's right pointer should be // current node. // 2. Node's right's left pointer should be // current node. // If one condition is met it is guaranteed // that the other condition is also true. return node.left != null && node.left.right == node && node.right != null && node.right.left == node; } // Compute the height of a tree static int findTreeHeight(Node node) { // if node is NULL return -1. if (node == null) return -1; // if node is a leaf node return 0 if (isLeaf(node)) return 0; // compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + Math.Max(findTreeHeight(node.left) findTreeHeight(node.right)); } static void Main(string[] args) { Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.left.left.left = new Node(6); // Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes Node l1 = root.left.left.left; Node l2 = root.left.right; Node l3 = root.right; // create circular doubly linked list out of // leaf nodes of the tree // set next pointer of linked list l1.right = l2; l2.right = l3; l3.right = l1; // set prev pointer of linked list l3.left = l2; l2.left = l1; l1.left = l3; Console.WriteLine(findTreeHeight(root)); } }
// JavaScript program to calculate height of a special tree // whose leaf nodes forms a circular doubly linked list class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // function to check if given // node is a leaf node or node function isLeaf(node) { // For a node to be a leaf node it should // satisfy the following two conditions: // 1. Node's left's right pointer should be // current node. // 2. Node's right's left pointer should be // current node. // If one condition is met it is guaranteed // that the other condition is also true. return node.left && node.left.right === node && node.right && node.right.left === node; } // Compute the height of a tree function findTreeHeight(node) { // if node is NULL return -1. if (node === null) return -1; // if node is a leaf node return 0 if (isLeaf(node)) return 0; // compute the depth of each subtree and take maximum return 1 + Math.max(findTreeHeight(node.left) findTreeHeight(node.right)); } const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.left.left.left = new Node(6); // Given tree contains 3 leaf nodes const l1 = root.left.left.left; const l2 = root.left.right; const l3 = root.right; // create circular doubly linked list out of // leaf nodes of the tree // set next pointer of linked list l1.right = l2; l2.right = l3; l3.right = l1; // set prev pointer of linked list l3.left = l2; l2.left = l1; l1.left = l3; console.log(findTreeHeight(root));
Lähtö
3
Aika monimutkaisuus: O(n) missä n on solmujen lukumäärä.
Aputila: Voi)


