Minimax on eräänlainen backtracking-algoritmi, jota käytetään päätöksenteossa ja peliteoriassa etsimään pelaajalle optimaalista liikettä olettaen, että myös vastustajasi pelaa optimaalisesti. Sitä käytetään laajalti kahden pelaajan vuoropohjaisissa peleissä, kuten Tic-Tac-Toe, Backgammon, Mancala, Shakki jne.
Minimaxissa näitä kahta pelaajaa kutsutaan maximizeriksi ja minimizeriksi. The maksimoija yrittää saada korkeimman mahdollisen pistemäärän minimointi yrittää tehdä päinvastoin ja saada mahdollisimman alhaiset pisteet.
Jokaiseen hallituksen tilaan liittyy arvo. Tietyssä tilassa, jos maksimoijalla on yliotto, taulun pistemäärä on yleensä jokin positiivinen arvo. Jos minimoijalla on yliotteen kyseisessä levytilassa, sillä on taipumus olla negatiivinen arvo. Lautan arvot lasketaan joidenkin heuristiikkojen avulla, jotka ovat ainutlaatuisia jokaiselle pelityypille.
Sree Ramanujan
Esimerkki:
Harkitse peliä, jossa on 4 lopputilaa ja polut lopulliseen tilaan saavuttamiseksi ovat täydellisen binääripuun juuresta 4 lehteen alla olevan kuvan mukaisesti. Oletetaan, että olet maksimoiva pelaaja ja saat ensimmäisen mahdollisuuden liikkua, eli olet juurilla ja vastustajasi seuraavalla tasolla. Minkä liikkeen tekisit maksimoivana pelaajana, kun otetaan huomioon, että myös vastustajasi pelaa optimaalisesti?
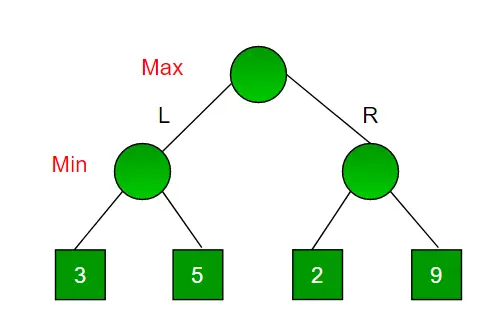
Koska tämä on paluupohjainen algoritmi, se yrittää kaikkia mahdollisia liikkeitä, sitten perääntyy ja tekee päätöksen.
- Maksimoija menee VASEMMALLE: Nyt on minimointien vuoro. Minimoijalla on nyt valinnanvaraa 3 ja 5 välillä. Minimoijana se valitsee ehdottomasti vähiten molemmista, eli 3
- Maksimoija menee OIKEALLE: Nyt on pienentäjien vuoro. Minimoijalla on nyt mahdollisuus valita 2 ja 9 välillä. Hän valitsee 2, koska se on pienin kahdesta arvosta.
Maksimoijana valitsisit suuremman arvon, joka on 3. Näin ollen maksimoijan optimaalinen liike on siirtyä VASEN ja optimaalinen arvo on 3.
Nyt pelipuu näyttää tältä:

Yllä oleva puu näyttää kaksi mahdollista pistemäärää, kun maksimitoiminto liikkuu vasemmalle ja oikealle.
Huomautus: Vaikka oikeanpuoleisessa alipuussa on arvo 9, minimoija ei koskaan valitse sitä. Meidän on aina oletettava, että vastustajamme pelaa optimaalisesti.
Alla on sama toteutus.
C++
// A simple C++ program to find> // maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is> // of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> int> minimax(>int> depth,>int> nodeIndex,>bool> isMax,> >int> scores[],>int> h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e> >// leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> >// If current move is maximizer,> >// find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>false>, scores, h));> >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>true>, scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> int> log2(>int> n)> {> >return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> // Driver code> int> main()> {> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >int> scores[] = {3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23};> >int> n =>sizeof>(scores)/>sizeof>(scores[0]);> >int> h = log2(n);> >int> res = minimax(0, 0,>true>, scores, h);> >cout <<>'The optimal value is : '> << res << endl;> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
Java
// A simple java program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> import> java.io.*;> class> GFG {> > // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> >static> int> minimax(>int> depth,>int> nodeIndex,>boolean> isMax,> >int> scores[],>int> h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> >// If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> Math.max(minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2>,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2> +>1>,>false>, scores, h));> >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> Math.min(minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2>,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2> +>1>,>true>, scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> >static> int> log2(>int> n)> {> return> (n==>1>)?>0> :>1> + log2(n/>2>);> }> // Driver code> >public> static> void> main (String[] args) {> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >int> scores[] = {>3>,>5>,>2>,>9>,>12>,>5>,>23>,>23>};> >int> n = scores.length;> >int> h = log2(n);> >int> res = minimax(>0>,>0>,>true>, scores, h);> >System.out.println(>'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > >}> }> // This code is contributed by vt_m> |
>
>
C#
// A simple C# program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> using> System;> public> class> GFG> {> > // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> static> int> minimax(>int> depth,>int> nodeIndex,>bool> isMax,> >int> []scores,>int> h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> >// If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> Math.Max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>false>, scores, h));> >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> Math.Min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>true>, scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> static> int> log2(>int> n)> {> >return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> // Driver code> static> public> void> Main ()> {> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >int> []scores = {3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23};> >int> n = scores.Length;> >int> h = log2(n);> >int> res = minimax(0, 0,>true>, scores, h);> >Console.WriteLine(>'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > }> }> // This code is contributed by ajit.> |
>
>
Python 3
# A simple Python3 program to find> # maximum score that> # maximizing player can get> import> math> def> minimax (curDepth, nodeIndex,> >maxTurn, scores,> >targetDepth):> ># base case : targetDepth reached> >if> (curDepth>=>=> targetDepth):> >return> scores[nodeIndex]> > >if> (maxTurn):> >return> max>(minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2>,> >False>, scores, targetDepth),> >minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2> +> 1>,> >False>, scores, targetDepth))> > >else>:> >return> min>(minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2>,> >True>, scores, targetDepth),> >minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2> +> 1>,> >True>, scores, targetDepth))> > # Driver code> scores>=> [>3>,>5>,>2>,>9>,>12>,>5>,>23>,>23>]> treeDepth>=> math.log(>len>(scores),>2>)> print>(>'The optimal value is : '>, end>=> '')> print>(minimax(>0>,>0>,>True>, scores, treeDepth))> # This code is contributed> # by rootshadow> |
>
>
Javascript
> // Javascript program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> >function> minimax(depth, nodeIndex, isMax,> >scores, h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> > >// If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> Math.max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>false>, scores, h));> > >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> Math.min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>true>, scores, h));> }> > // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> >function> log2(n)> {> return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> > // Driver Code> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >let scores = [3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23];> >let n = scores.length;> >let h = log2(n);> >let res = minimax(0, 0,>true>, scores, h);> >document.write(>'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > > > |
>
>
Lähtö:
The optimal value is: 12>
Aika monimutkaisuus: O(b^d) b on haarautumiskerroin ja d on graafin tai puun syvyyden tai kerrosluku.
Avaruuden monimutkaisuus: O(bd), jossa b on haarautumiskerroin d:hen, on puun suurin syvyys, joka on samanlainen kuin DFS.
Tämän artikkelin ideana on esitellä Minimax yksinkertaisella esimerkillä.
- Yllä olevassa esimerkissä pelaajalla on vain kaksi vaihtoehtoa. Yleensä vaihtoehtoja voi olla enemmän. Siinä tapauksessa meidän on toistettava kaikki mahdolliset liikkeet ja löydettävä maksimi/minimi. Esimerkiksi Tic-Tac-Toe-pelissä ensimmäinen pelaaja voi tehdä 9 mahdollista siirtoa.
- Yllä olevassa esimerkissä pisteet (riistapuun lehdet) annetaan meille. Tyypillisessä pelissä meidän on johdettava nämä arvot
Katamme pian Tic Tac Toen Minimax-algoritmilla.
Tämän artikkelin on kirjoittanut Akshay L. Aradhya.
