Voimme luoda java-ohjelman lajittelemaan taulukon elementtejä valintalajittelun avulla. Valintalajittelualgoritmissa etsimme alimman elementin ja järjestämme sen oikeaan paikkaan. Vaihdamme nykyisen elementin seuraavaksi pienimpään numeroon.
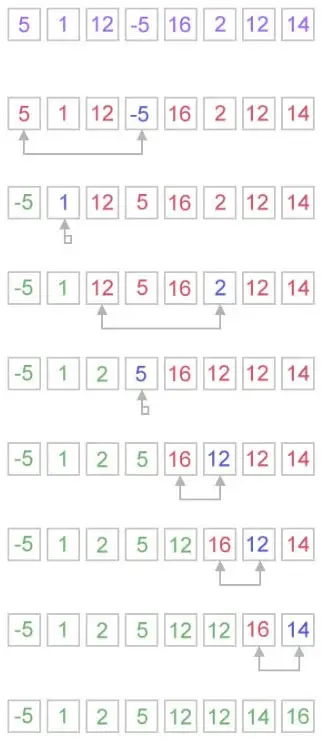
Miten valintalajittelu toimii?
Valintalajittelualgoritmi toimii hyvin yksinkertaisella tavalla. Se ylläpitää kahta alitaulukkoa annetulle taulukolle.
eteenpäin ketjuttaminen
- Alaryhmä on jo lajiteltu.
- Ja toinen aliryhmä on lajittelematon.
Jokaisella valintalajittelun iteraatiolla elementti poimitaan lajittelemattomasta alitaulukosta ja siirretään lajiteltuun alitaulukkoon.
hei maailma javalla
arr[] = 25 35 45 12 65 10 // Find the minimum element in arr[0...5] and place it at beginning. 10 25 35 45 12 65 // Find the minimum element in arr[1...5] and place it at beginning of arr[1...5] 10 12 25 35 45 65 // Find the minimum element in arr[2...5] and place it at beginning of arr[2...5] No, you can see that the array is already sorted. 10 12 25 35 45 65
Aika monimutkaisuus
Parhaat: ?(n^2)Keskiverto: ?(n^2)
Huonoin: O(n^2)
Avaruuden monimutkaisuus
O(1)Valinta Lajittele Java-esimerkki
public class SelectionSortExample { public static void selectionSort(int[] arr){ for (int i = 0; i <arr.length - 1; i++) { int index="i;" for (int j="i" + < arr.length; j++){ if (arr[j] arr[index]){ lowest } smallernumber="arr[index];" arr[index]="arr[i];" arr[i]="smallerNumber;" public static void main(string a[]){ int[] arr1="{9,14,3,2,43,11,58,22};" system.out.println('before selection sort'); for(int i:arr1){ system.out.print(i+' '); system.out.println(); selectionsort(arr1); sorting array using sort system.out.println('after pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Before Selection Sort 9 14 3 2 43 11 58 22 After Selection Sort 2 3 9 11 14 22 43 58 </pre> <h2>Selection Sort in Java (Another way)</h2> <p>You can also use a method where array is not predefined. Here, user has to put the elements as input.</p> <p>In the following Java program, we ask user to enter the array elements or number, now compare the array's element and start swapping with the variable temp. Put the first element in the temp and the second element in the first, and then temp in the second number and continue for the next match to sort the whole array in ascending order.</p> <pre> import java.util.Scanner; public class SelectionSortExample2 { public static void main(String args[]) { int size, i, j, temp; int arr[] = new int[50]; Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print('Enter Array Size : '); size = scan.nextInt(); System.out.print('Enter Array Elements : '); for(i=0; i<size; i++) { arr[i]="scan.nextInt();" } system.out.print('sorting array using selection sort technique..
'); for(i="0;" i<size; for(j="i+1;" j arr[j]) temp="arr[i];" arr[j]="temp;" system.out.print('now the after sorting is :
'); system.out.print(arr[i]+ ' '); < pre> <p>Output:</p> <strong> Use image SelectionSort</strong> </size;></pre></arr.length> Valinnan lajittelu Javassa (toinen tapa)
Voit myös käyttää menetelmää, jossa taulukkoa ei ole ennalta määritetty. Täällä käyttäjän on asetettava elementit syötteeksi.
Seuraavassa Java-ohjelmassa pyydämme käyttäjää syöttämään taulukon elementit tai numeron, vertaa nyt taulukon elementtiä ja aloita vaihtaminen muuttujalla temp. Laita ensimmäinen elementti temp-arvoon ja toinen elementti ensimmäiseen ja sitten temp toiseen numeroon ja jatka seuraavaan osumaan lajitellaksesi koko taulukon nousevaan järjestykseen.
import java.util.Scanner; public class SelectionSortExample2 { public static void main(String args[]) { int size, i, j, temp; int arr[] = new int[50]; Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print('Enter Array Size : '); size = scan.nextInt(); System.out.print('Enter Array Elements : '); for(i=0; i<size; i++) { arr[i]="scan.nextInt();" } system.out.print(\'sorting array using selection sort technique..
\'); for(i="0;" i<size; for(j="i+1;" j arr[j]) temp="arr[i];" arr[j]="temp;" system.out.print(\'now the after sorting is :
\'); system.out.print(arr[i]+ \' \'); < pre> <p>Output:</p> <strong> Use image SelectionSort</strong> </size;>