Binäärinen puu on puutyyppinen epälineaarinen tietorakenne, jota käytetään pääasiassa lajitteluun ja hakuun, koska ne tallentavat tiedot hierarkkisessa muodossa. Tässä osiossa opimme binaaripuun tietorakenteen toteutus Javassa . Tarjoaa myös lyhyen kuvauksen binääripuun tietorakenteesta.
Binääripuu
Puuta, jossa jokaisella solmulla (vanhemmalla) on enintään kaksi lapsisolmua (vasen ja oikea), kutsutaan binääripuuksi. Ylintä solmua kutsutaan juurisolmuksi. Binääripuussa solmu sisältää tiedot sekä vasemman ja oikean lapsisolmun tiedot ja osoittimen (osoitteen).
kehittäjätilan poistaminen käytöstä
The korkeus binääripuusta on puun juuren välisten reunojen lukumäärä ja sen kauimpana (syvimpänä) lehtinä. Jos puu on tyhjä , korkeus on 0 . Solmun korkeutta merkitään h .
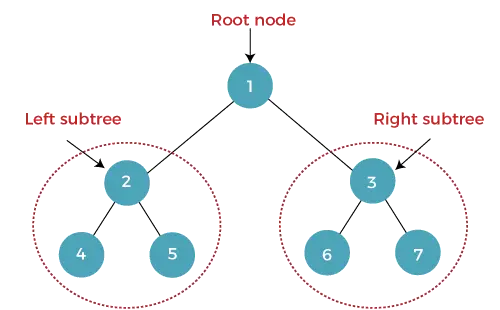
Yllä olevan binääripuun korkeus on 2.
Voimme laskea lehtien ja solmun lukumäärän seuraavan kaavan avulla.
- Lehtisolmujen enimmäismäärä on binääripuu: 2h
- Solmujen enimmäismäärä on binääripuu: 2h+1-1
Missä h on binääripuun korkeus.
Esimerkki binaaripuusta

Binääripuutyypit
Tietorakenteessa on seuraavan tyyppisiä binääripuita:
- Täysi / tiukasti binaarinen puu
- Täydellinen binääripuu
- Täydellinen binaaripuu
- Tasapainottaa binaaripuuta
- Juurtunut binääripuu
- Degeneroitunut / patologinen binaaripuu
- Laajennettu binääripuu
- Vino binääripuu
- Vasemmalle vino binaaripuu
- Oikealle vino binaaripuu
- Kierteitetty binääripuu
- Yksisäikeinen binaaripuu
- Kaksisäikeinen binaaripuu
Binaaripuun toteutus Javassa
Binääripuun toteuttamiseen on monia tapoja. Tässä osiossa toteutamme binääripuun käyttämällä LinkedList-tietorakennetta. Sen lisäksi toteutamme myös läpikulkukäskyt, etsimällä solmun ja lisäämällä solmun binääripuuhun.
Binaaripuun käyttöönotto LinkedListin avulla
Algoritmi
Määrittele Node-luokka, joka sisältää kolme attribuuttia, nimittäin: data vasen ja oikea. Tässä vasen edustaa solmun vasenta lasta ja oikea edustaa solmun oikeaa lasta.
- Kun solmu luodaan, tiedot siirtyvät solmun dataattribuutille ja sekä vasen että oikea arvo asetetaan nollaksi.
- Määrittele toinen luokka, jolla on määritteen juuri.
- Juuri edustaa puun juurisolmua ja alustaa sen nollaksi.
- Se tarkistaa, onko juuri nolla, mikä tarkoittaa, että puu on tyhjä. Se lisää uuden solmun pääkäyttäjäksi.
- Muuten se lisää juuren jonoon.
- Muuttujasolmu edustaa nykyistä solmua.
- Ensin se tarkistaa, onko solmulla vasen ja oikea lapsi. Jos kyllä, se lisää molemmat solmut jonoon.
- Jos vasen ali ei ole läsnä, se lisää uuden solmun vasemmaksi lapseksi.
- Jos vasen on läsnä, se lisää uuden solmun oikeaksi lapsiksi.
- Se kulkee koko puun läpi ja tulostaa sitten vasemman alaosan, jota seuraa juuri ja sen jälkeen oikea lapsi.
BinarySearchTree.java
public class BinarySearchTree { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node{ int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data){ //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public BinarySearchTree(){ root = null; } //factorial() will calculate the factorial of given number public int factorial(int num) { int fact = 1; if(num == 0) return 1; else { while(num > 1) { fact = fact * num; num--; } return fact; } } //numOfBST() will calculate the total number of possible BST by calculating Catalan Number for given key public int numOfBST(int key) { int catalanNumber = factorial(2 * key)/(factorial(key + 1) * factorial(key)); return catalanNumber; } public static void main(String[] args) { BinarySearchTree bt = new BinarySearchTree(); //Display total number of possible binary search tree with key 5 System.out.println('Total number of possible Binary Search Trees with given key: ' + bt.numOfBST(5)); } } Lähtö:
Binary tree after insertion 1 Binary tree after insertion 2 1 3 Binary tree after insertion 4 2 5 1 3 Binary tree after insertion 4 2 5 1 6 3 7
Binääripuutoiminnot
Seuraavat toiminnot voidaan suorittaa binääripuulle:
- Lisäys
- Poistaminen
- Hae
- Läpikulku
Java-ohjelma solmun lisäämiseksi binaaripuuhun
BinaryTreeInsert.java
public class BinaryTreeInsert { public static void main(String[] args) { new BinaryTreeInsert().run(); } static class Node { Node left; Node right; int value; public Node(int value) { this.value = value; } } public void run() { Node rootnode = new Node(25); System.out.println('Building tree with root value ' + rootnode.value); System.out.println('================================='); insert(rootnode, 11); insert(rootnode, 15); insert(rootnode, 16); insert(rootnode, 23); insert(rootnode, 79); } public void insert(Node node, int value) { if (value node.value) { if (node.right != null) { insert(node.right, value); } else { System.out.println(' Inserted ' + value + ' to right of Node ' + node.value); node.right = new Node(value); } } } } Lähtö:
Building tree with root value 25 ================================= Inserted 11 to left of Node 25 Inserted 15 to right of Node 11 Inserted 16 to right of Node 15 Inserted 23 to right of Node 16 Inserted 79 to right of Node 25
Java-ohjelma solmun poistamiseksi Javassa
Algoritmi
- Alkaen juuresta, etsi binääripuun syvin ja oikeanpuoleisin solmu ja solmu, jonka haluamme poistaa.
- Korvaa syvimmän oikeanpuoleisen solmun tiedot poistettavalla solmulla.
- Poista sitten syvin oikealla oleva solmu.
Harkitse seuraavaa kuvaa.

DeleteNode.java
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class DeleteNode { // A binary tree node has key, pointer to // left child and a pointer to right child static class Node { int key; Node left, right; // Constructor Node(int key) { this.key = key; left = null; right = null; } } static Node root; static Node temp = root; // Inorder traversal of a binary tree static void inorder(Node temp) { if (temp == null) return; inorder(temp.left); System.out.print(temp.key + ' '); inorder(temp.right); } // Function to delete deepest // element in binary tree static void deleteDeepest(Node root, Node delNode) { Queue q = new LinkedList(); q.add(root); Node temp = null; // Do level order traversal until last node while (!q.isEmpty()) { temp = q.peek(); q.remove(); if (temp == delNode) { temp = null; return; } if (temp.right!=null) { if (temp.right == delNode) { temp.right = null; return; } else q.add(temp.right); } if (temp.left != null) { if (temp.left == delNode) { temp.left = null; return; } else q.add(temp.left); } } } // Function to delete given element // in binary tree static void delete(Node root, int key) { if (root == null) return; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { if (root.key == key) { root=null; return; } else return; } Queue q = new LinkedList(); q.add(root); Node temp = null, keyNode = null; // Do level order traversal until // we find key and last node. while (!q.isEmpty()) { temp = q.peek(); q.remove(); if (temp.key == key) keyNode = temp; if (temp.left != null) q.add(temp.left); if (temp.right != null) q.add(temp.right); } if (keyNode != null) { int x = temp.key; deleteDeepest(root, temp); keyNode.key = x; } } // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(11); root.left.left = new Node(7); root.left.right = new Node(12); root.right = new Node(9); root.right.left = new Node(15); root.right.right = new Node(8); System.out.print('Inorder traversal before deletion: '); inorder(root); //node to delete int key = 7; delete(root, key); System.out.print('
Inorder traversal after deletion: '); inorder(root); } } Lähtö:
bash-muuttuja
Inorder traversal before deletion: 7 11 12 10 15 9 8 Inorder traversal after deletion: 8 11 12 10 15 9
Java-ohjelma solmun etsimiseen binaaripuussa
Algoritmi
- Määrittele Node-luokka, jolla on kolme attribuuttia, nimittäin: data vasen ja oikea. Tässä vasen edustaa solmun vasenta lasta ja oikea edustaa solmun oikeaa lasta.
- Kun solmu luodaan, tiedot siirtyvät solmun dataattribuutille ja sekä vasen että oikea arvo asetetaan nollaksi.
- Määrittele toinen luokka, jolla on kaksi attribuuttia root ja lippu.
- Root edustaa puun juurisolmua ja alustaa sen nollaksi.
- Lippua käytetään tarkistamaan, onko annettu solmu puussa vai ei. Aluksi se asetetaan epätosi.
- Se tarkistaa, onko juuri nolla, mikä tarkoittaa, että puu on tyhjä.
- Jos puu ei ole tyhjä, se vertaa lämpötilan tietoja arvoon. Jos ne ovat yhtä suuret, se asettaa lipun tosi ja palauttaa.
- Kulje vasemman alipuun läpi kutsumalla searchNode() rekursiivisesti ja tarkista onko arvo vasemmassa alipuussa.
- Käy läpi oikea alipuu kutsumalla searchNode() rekursiivisesti ja tarkista onko arvo oikeassa alipuussa.
SearchBinaryTree.java
public class SearchBinaryTree { //Represent a node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public static boolean flag = false; public SearchBinaryTree() { root = null; } //searchNode() will search for the particular node in the binary tree public void searchNode(Node temp, int value) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); } else { //If value is found in the given binary tree then, set the flag to true if(temp.data == value) { flag = true; return; } //Search in left subtree if(flag == false && temp.left != null) { searchNode(temp.left, value); } //Search in right subtree if(flag == false && temp.right != null) { searchNode(temp.right, value); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { SearchBinaryTree bt = new SearchBinaryTree(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(11); bt.root.left = new Node(8); bt.root.right = new Node(12); bt.root.left.left = new Node(78); bt.root.right.left = new Node(23); bt.root.right.right = new Node(36); //Search for node 5 in the binary tree bt.searchNode(bt.root, 23); if(flag) System.out.println('Element is present in the binary tree.'); else System.out.println('Element is not present in the binary tree.'); } } Lähtö:
Element is present in the binary tree.
Binaaripuun läpikulku
| Läpikulkutilaus | Ensimmäinen käynti | Toinen vierailu | Kolmas käynti |
|---|---|---|---|
| Järjestyksessä | Siirry vasemmalle alipuulle järjestysjärjestyksessä | Vieraile juurisolmussa | Siirry oikeassa alipuussa järjestysjärjestyksessä |
| Ennakkotilaus | Vieraile juurisolmussa | Käy vasemmassa alipuussa ennakkotilauksessa | Siirry oikeaan alipuuhun ennakkotilauksessa |
| Postimyynti | Vieraile vasemmassa alipuussa postorderissa | Siirry oikeanpuoleiseen alipuuhun postorderissa | Vieraile juurisolmussa |
Huomautus: Edellä mainittuja kolmea läpikulkua lukuun ottamatta on olemassa toinenkin läpikulkujärjestys, jota kutsutaan rajan läpikulkuksi.
Java-ohjelma Inorder-, ennakkotilaus- ja jälkikäyttäytymiseen
BinaryTree.java
public class BinaryTree { // first node private Node root; BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Class representing tree nodes static class Node { int value; Node left; Node right; Node(int value) { this.value = value; left = null; right = null; } public void displayData() { System.out.print(value + ' '); } } public void insert(int i) { root = insert(root, i); } //Inserting node - recursive method public Node insert(Node node, int value) { if(node == null){ return new Node(value); } // Move to the left if passed value is // less than the current node if(value node.value) { node.right = insert(node.right, value); } return node; } // Search node in binary search tree public Node find(int searchedValue) { Node current = root; while(current.value != searchedValue) { if(searchedValue = current = current.right; if(current == null) { return null; } } return current; } // For traversing in order public void inOrder(Node node) { if(node != null) { inOrder(node.left); node.displayData(); inOrder(node.right); } } // Preorder traversal public void preOrder(Node node) { if(node != null){ node.displayData(); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } // Postorder traversal public void postOrder(Node node) { if(node != null) { postOrder(node.left); postOrder(node.right); node.displayData(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree bst = new BinaryTree(); bst.insert(34); bst.insert(56); bst.insert(12); bst.insert(89); bst.insert(67); bst.insert(90); System.out.println('Inorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.inOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); System.out.println('Preorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.preOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); System.out.println('Postorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.postOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); } } Lähtö:
Inorder traversal of binary tree 12 34 56 67 89 90 Preorder traversal of binary tree 34 12 56 89 67 90 Postorder traversal of binary tree 12 67 90 89 56 34
Yllä olevien toimintojen lisäksi voimme suorittaa myös operaatioita, kuten suuri solmu, pienin solmu ja kaikkien solmujen summa.
Java-ohjelma binaaripuun suurimman solmun löytämiseksi
SuurinNode.java
public class LargestNode { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public LargestNode() { root = null; } //largestElement() will find out the largest node in the binary tree public int largestElement(Node temp) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { int leftMax, rightMax; //Max will store temp's data int max = temp.data; //It will find largest element in left subtree if(temp.left != null){ leftMax = largestElement(temp.left); //Compare max with leftMax and store greater value into max max = Math.max(max, leftMax); } //It will find largest element in right subtree if(temp.right != null){ rightMax = largestElement(temp.right); //Compare max with rightMax and store greater value into max max = Math.max(max, rightMax); } return max; } } public static void main(String[] args) { LargestNode bt = new LargestNode(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(90); bt.root.left = new Node(99); bt.root.right = new Node(23); bt.root.left.left = new Node(96); bt.root.right.left = new Node(45); bt.root.right.right = new Node(6); bt.root.right.left = new Node(13); bt.root.right.right = new Node(77); //Display largest node in the binary tree System.out.println('Largest element in the binary tree: ' + bt.largestElement(bt.root)); } } Lähtö:
Largest element in the binary tree: 99
Java-ohjelma binaaripuun pienimmän solmun löytämiseksi
Algoritmi
- Määrittele Node-luokka, jolla on kolme attribuuttia, nimittäin data, vasen ja oikea. Tässä vasen edustaa solmun vasenta lasta ja oikea edustaa solmun oikeaa lasta.
- Kun solmu luodaan, tiedot siirretään solmun dataattribuutille ja sekä vasen että oikea arvo asetetaan nollaksi.
- Määrittele toinen luokka, jolla on määritteen juuri.
Juuri edustaa puun juurisolmua ja alusta sen nollaksi.
- Se tarkistaa onko root on nolla , mikä tarkoittaa, että puu on tyhjä.
- Jos puu ei ole tyhjä, määritä muuttuja min, joka tallentaa temp-tiedot.
- Selvitä vasemman alipuun minimisolmu kutsumalla smallestElement() rekursiivisesti. Tallenna tämä arvo kohtaan leftMin. Vertaa min arvoa leftMin:iin ja tallenna minimiarvo kahdesta min.
- Selvitä oikean alipuun vähimmäissolmu kutsumalla smallestElement() rekursiivisesti. Tallenna tämä arvo kohtaan rightMin. Vertaa min arvoa rightMin-arvoon ja tallenna maksimiarvo kahdesta min.
- Lopussa min sisältää binääripuun pienimmän solmun.
SmallestNode.java
public class SmallestNode { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public SmallestNode() { root = null; } //smallestElement() will find out the smallest node in the binary tree public int smallestElement(Node temp) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { int leftMin, rightMin; //Min will store temp's data int min = temp.data; //It will find smallest element in left subtree if(temp.left != null) { leftMin = smallestElement(temp.left); //If min is greater than leftMin then store the value of leftMin into min min = Math.min(min, leftMin); } //It will find smallest element in right subtree if(temp.right != null) { rightMin = smallestElement(temp.right); //If min is greater than rightMin then store the value of rightMin into min min = Math.min(min, rightMin); } return min; } } public static void main(String[] args) { SmallestNode bt = new SmallestNode(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(9); bt.root.left = new Node(5); bt.root.right = new Node(7); bt.root.left.left = new Node(1); bt.root.right.left = new Node(2); bt.root.right.right = new Node(8); bt.root.right.left = new Node(4); bt.root.right.right = new Node(3); //Display smallest node in the binary tree System.out.println('Smallest element in the binary tree: ' + bt.smallestElement(bt.root)); } } Lähtö:
Smallest element in the binary tree: 1
Java-ohjelma binaaripuun enimmäisleveyden löytämiseksi
Algoritmi
- Määrittele Node-luokka, jolla on kolme attribuuttia, nimittäin: data vasen ja oikea. Tässä vasen edustaa solmun vasenta lasta ja oikea edustaa solmun oikeaa lasta.
- Kun solmu luodaan, tiedot siirtyvät solmun dataattribuutille ja sekä vasen että oikea arvo asetetaan nollaksi.
- Määrittele toinen luokka, jolla on määritteen juuri.
Juuri edustaa puun juurisolmua ja alustaa sen nollaksi.
- Muuttuja maxWidth tallentaa suurimman mahdollisen määrän solmuja millä tahansa tasolla.
- Jonoa käytetään binääripuun läpikulkuun tasoittain.
- Se tarkistaa, onko juuri nolla, mikä tarkoittaa, että puu on tyhjä.
- Jos ei, lisää juurisolmu jonoon. Variable nodesInLevel pitää kirjaa kunkin tason solmujen määrästä.
- Jos nodesInLevel > 0, poista solmu jonon etuosasta ja lisää sen vasen ja oikea lapsi jonoon. Ensimmäisessä iteraatiossa solmu 1 poistetaan ja sen alisolmut 2 ja 3 lisätään jonoon. Toisessa iteraatiossa solmu 2 poistetaan, sen lapset 4 ja 5 lisätään jonoon ja niin edelleen.
- MaxWidth tallentaa max(maxWidth, nodesInLevel). Joten milloin tahansa se edustaa solmujen enimmäismäärää.
- Tämä jatkuu, kunnes kaikki puun tasot on ylitetty.
BinaryTree.java
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class BinaryTree { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public BinaryTree() { root = null; } //findMaximumWidth() will find out the maximum width of the given binary tree public int findMaximumWidth() { int maxWidth = 0; //Variable nodesInLevel keep tracks of number of nodes in each level int nodesInLevel = 0; //queue will be used to keep track of nodes of tree level-wise Queue queue = new LinkedList(); //Check if root is null, then width will be 0 if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { //Add root node to queue as it represents the first level queue.add(root); while(queue.size() != 0) { //Variable nodesInLevel will hold the size of queue i.e. number of elements in queue nodesInLevel = queue.size(); //maxWidth will hold maximum width. //If nodesInLevel is greater than maxWidth then, maxWidth will hold the value of nodesInLevel maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, nodesInLevel); //If variable nodesInLevel contains more than one node //then, for each node, we'll add left and right child of the node to the queue while(nodesInLevel > 0) { Node current = queue.remove(); if(current.left != null) queue.add(current.left); if(current.right != null) queue.add(current.right); nodesInLevel--; } } } return maxWidth; } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(1); bt.root.left = new Node(2); bt.root.right = new Node(3); bt.root.left.left = new Node(4); bt.root.left.right = new Node(5); bt.root.right.left = new Node(6); bt.root.right.right = new Node(7); bt.root.left.left.left = new Node(8); //Display the maximum width of given tree System.out.println('Maximum width of the binary tree: ' + bt.findMaximumWidth()); } } Lähtö:
Maximum width of the binary tree: 4
