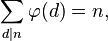Eulerin Totient-funktio Φ(n) syötteelle n on niiden lukujen määrä yksiköissä {1, 2, 3, …, n-1}, jotka ovat suhteellisesti alkulukuja n:ään nähden, eli luvut, joiden GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) on n:llä on 1.
Esimerkkejä:
Φ(1) = 1
gcd(1, 1) on 1
Φ(2) = 1
gcd(1, 2) on 1, mutta gcd(2, 2) on 2.
Φ(3) = 2
gcd(1, 3) on 1 ja gcd(2, 3) on 1
Φ(4) = 2
gcd(1, 4) on 1 ja gcd(3, 4) on 1
Φ(5) = 4
gcd(1, 5) on 1, gcd(2, 5) on 1,
gcd(3, 5) on 1 ja gcd(4, 5) on 1
Φ(6) = 2
gcd(1, 6) on 1 ja gcd(5, 6) on 1,
Suositeltu käytäntö Euler Totient -toiminto Kokeile sitä!
Miten lasketaan Φ(n) syötteelle n?
A yksinkertainen ratkaisu on iteroida kaikki luvut 1:stä n-1:een ja laskea luvut gcd:llä, jossa n on 1. Alla on toteutettu yksinkertainen menetelmä Eulerin Totient-funktion laskemiseksi syötetylle kokonaisluvulle n.
// A simple C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Java // A simple java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by sunnusingh>Python 3 # A simple Python3 program # to calculate Euler's # Totient Function # Function to return # gcd of a and b def gcd(a, b): if (a == 0): return b return gcd(b % a, a) # A simple method to evaluate # Euler Totient Function def phi(n): result = 1 for i in range(2, n): if (gcd(i, n) == 1): result+=1 return result # Driver Code for n in range(1, 11): print('phi(',n,') = ', phi(n), sep = '') # This code is contributed # by Smitha>C# // A simple C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void Main() { for (int n = 1; n <= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal>Javascript >>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // Function to return // gcd of a and b function gcd($a, $b) { if ($a == 0) return $b; return gcd($b % $a, $a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function function phi($n) { $result = 1; for ($i = 2; $i <$n; $i++) if (gcd($i, $n) == 1) $result++; return $result; } // Driver Code for ($n = 1; $n <= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>>>C++ // A simple C++ program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function #include using namespace std; // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) cout << 'phi('<
Lähtö phi(1) = 1 phi(2) = 1 phi(3) = 2 phi(4) = 2 phi(5) = 4 phi(6) = 2 phi(7) = 6 phi(8) = 4 phi( 9) = 6 phi(10) = 4
Yllä oleva koodi kutsuu gcd-funktiota O(n) kertaa. Gcd-funktion aikamonimutkaisuus on O(h), jossa h on numeroiden lukumäärä pienemmässä määrässä annettua kahta numeroa. Siksi yläraja aika monimutkaisuus yllä olevasta ratkaisusta on O(N^2 log N) [Kuinka Φ voi olla enintään Log10n numeroa kaikissa numeroissa 1 - n]
Aputila: O(log N)
Alla on a Parempi Ratkaisu . Idea perustuu Eulerin tuotekaavaan, jossa todetaan, että kokonaisfunktioiden arvo on alle tuotteen kokonaisalkutekijät p n:stä.
Kaava sanoo periaatteessa, että Φ(n):n arvo on yhtä suuri kuin n kerrottuna (1 – 1/p):n sivutuote kaikille n:n alkutekijöille p. Esimerkiksi Φ(6) = 6 * (1-1/2) * (1 - 1/3) = 2.
Voimme löytää kaikki alkutekijät käyttämällä ideaa, jota käytetään Tämä lähettää.
1) Alusta : tulos = n
2) Suorita silmukka arvosta 'p' = 2 arvoon sqrt(n), tee seuraava jokaiselle 'p':lle.
a) Jos p jakaa n:n, niin
Joukko: tulos = tulos * (1,0 - (1,0 / (float) p));
Jaa kaikki p:n esiintymät n:llä.
3) Palautustulos
merkkijono int-muunnin
Alla on Eulerin tuotekaavan toteutus.
C++ // C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function using Euler's // product formula #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and for every prime factor p, // multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) tulos -= tulos / n; //Koska joukossa {1,2,....,n-1}, kaikki luvut ovat suhteellisen alkulukuja n:n kanssa //jos n on alkuluku palauttaa (int)tulos; } // Ohjainkoodi int main() { int n; for(n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) <C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula #include int phi(int n) { float result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) tulos -= tulos / n; //Koska joukossa {1,2,....,n-1}, kaikki luvut ovat suhteellisen alkulukuja n:n kanssa //jos n on alkuluku palauttaa (int)tulos; } // Ohjainohjelma yllä olevan funktion testaamiseen int main() { int n; varten (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Java // Java program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n and for // every prime factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) tulos -= tulos / n; //Koska joukossa {1,2,....,n-1}, kaikki luvut ovat suhteellisen alkulukuja n:n kanssa //jos n on alkuluku palauttaa (int)tulos; } // Ohjainohjelma yllä olevan toiminnon testaamiseen public static void main(String args[]) { int n; varten (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.>Python 3 # Python 3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function # using Euler's product formula def phi(n) : result = n # Initialize result as n # Consider all prime factors # of n and for every prime # factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1 / p) p = 2 while p * p<= n : # Check if p is a prime factor. if n % p == 0 : # If yes, then update n and result while n % p == 0 : n = n // p result = result * (1.0 - (1.0 / float(p))) p = p + 1 # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most one # such prime factor) if n>1 : tulos -= tulos // n #Koska joukossa {1,2,....,n-1}, kaikki luvut ovat suhteellisen alkulukuja n:n kanssa #jos n on alkuluku palauttaa int(tulos) # Ohjain ohjelma testaamaan yllä olevaa funktiota n:lle alueella(1, 11): print('phi(', n, ') = ', phi(n)) # Tämän koodin on toimittanut # Nikita Tiwari.>>C# // C# program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1 / p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (float)(1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) tulos -= tulos / n; //Koska joukossa {1,2,....,n-1}, kaikki luvut ovat suhteellisen alkulukuja n:n kanssa //jos n on alkuluku palauttaa (int)tulos; } // Ohjainkoodi public static void Main() { int n; varten (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.>Javascript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi(n) { // Initialize result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) tulos -= tulos / n; //Koska joukossa {1,2,....,n-1}, kaikki luvut ovat suhteellisen alkulukuja n:n kanssa //jos n on alkuluku return parseInt(result); } // Ohjainkoodi kohteelle (olkoon n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi($n) { // Initialize result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n /= $p; $result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / $p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $tulos -= $tulos / $n; //Koska joukossa {1,2,....,n-1}, kaikki luvut ovat suhteellisen alkulukuja n:n kanssa //jos n on alkuluku return intval($tulos); } // Ohjainkoodi kohteelle ($n = 1; $n<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>>>
Lähtö Phi(1) = 1 Phi(2) = 1 Phi(3) = 2 Phi(4) = 2 Phi(5) = 4 Phi(6) = 2 Phi(7) = 6 Phi(8) = 4 Phi( 9) = 6 Phi(10) = 4
Aika monimutkaisuus: O(Φ n log n)
Aputila: O(1)
Voimme välttää liukulukulaskutoimitukset yllä olevalla menetelmällä. Ajatuksena on laskea kaikki alkutekijät ja niiden kerrannaiset ja vähentää tämä luku n:stä saadaksesi kokonaisfunktion arvon (Alkutekijöiden ja alkutekijöiden kerrannaisten gcd ei ole 1)
1) Alusta tulokseksi n
2) Tarkastellaan jokaista lukua 'p' (missä 'p' vaihtelee 2:sta Φ(n)).
Jos p jakaa n:n, toimi seuraavasti
a) Vähennä p:n kaikki kerrannaiset luvusta 1 arvoon n [kaikki p:n kerrannaiset
on gcd enemmän kuin 1 (vähintään p) ja n]
b) Päivitä n jakamalla se toistuvasti p:llä.
3) Jos pelkistetty n on suurempi kuin 1, poista kaikki kerrannaisuudet
n:stä tuloksesta.
Alla on yllä olevan algoritmin toteutus.
C++ // C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and subtract their multiples // from result for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) tulos -= tulos / n; palauttaa tuloksen; } // Ohjainkoodi int main() { int n; for(n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) << endl; } return 0; } // This code is contributed by koulick_sadhu>C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include int phi(int n) { int result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) tulos -= tulos / n; palauttaa tuloksen; } // Ohjainohjelma yllä olevan funktion testaamiseen int main() { int n; varten (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Java // Java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) tulos -= tulos / n; palauttaa tuloksen; } // Ohjainkoodi public static void main (String[] args) { int n; varten (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by ajit>Python 3 # Python3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function def phi(n): # Initialize result as n result = n; # Consider all prime factors # of n and subtract their # multiples from result p = 2; while(p * p <= n): # Check if p is a # prime factor. if (n % p == 0): # If yes, then # update n and result while (n % p == 0): n = int(n / p); result -= int(result / p); p += 1; # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most # one such prime factor) if (n>1): tulos -= int(tulos / n); palauttaa tuloksen; # Ohjainkoodi n:lle alueella(1, 11): print('phi(',n,') =', phi(n)); # Tämän koodin # on toimittanut mits>>C# // C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and // subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) tulos -= tulos / n; palauttaa tuloksen; } // Ohjainkoodi staattinen public void Main () { int n; varten (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed // by akt_mit>Javascript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi(n) { // Initialize // result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while (n % p == 0) n = parseInt(n / p); result -= parseInt(result / p); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) tulos -= parseInt(tulos / n); palauttaa tuloksen; } // Ohjainkoodi kohteelle (olkoon n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed // by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi($n) { // Initialize // result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n = (int)$n / $p; $result -= (int)$result / $p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $tulos -= (int)$tulos / $n; palauttaa $tulos; } // Ohjainkoodi kohteelle ($n = 1; $n<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(', $n,') =', phi($n), '
'; // This code is contributed // by ajit Φ>>>
Lähtö Phi(1) = 1 Phi(2) = 1 Phi(3) = 2 Phi(4) = 2 Phi(5) = 4 Phi(6) = 2 Phi(7) = 6 Phi(8) = 4 Phi( 9) = 6 Phi(10) = 4
Aika monimutkaisuus: O(Φ n log n)
Aputila: O(1)
Otetaan esimerkki yllä olevan algoritmin ymmärtämiseksi.
n = 10.
Alusta: tulos = 10
2 on alkutekijä, joten n = n/i = 5, tulos = 5
3 ei ole ensisijainen tekijä.
For-silmukka pysähtyy 3:n jälkeen, koska 4*4 ei ole pienempi tai yhtä suuri
10:een.
For-silmukan jälkeen tulos = 5, n = 5
Koska n> 1, tulos = tulos - tulos/n = 4
Jotkut Eulerin Totient-funktion mielenkiintoiset ominaisuudet
1) a alkuluku s ,phi(p) = p – 1
Todiste :
missä k on mikä tahansa satunnaisluku jaKokonaisluku 1:stä p = p Luku, jolle, eli itse luku p, joten p:stä vähennetään 1phi(p) = p - 1
Esimerkkejä:
phi(5) = 5 - 1 = 4 phi(13) = 13 - 1 = 12 phi(29) = 29 - 1 = 28
2) varten kaksi alkulukua a ja b phi(a cdot b) = phi(a) cdot phi(b) = (a – 1) cdot (b – 1) , käytetty RSA-algoritmi
Todiste :
phi(acdot b) = phi(a) cdot phi(b) , jossa a ja b ovat alkulukujaphi(a) = a - 1 ,phi(b) = b - 1 frac{a cdot b} {a} =b B:n kokonaiskerrat arvosta 1 arvoon ab =frac{a cdot b} {b} =a Esimerkki: a = 5, b = 7, ab = 35 A = kerrannaisetfrac {35} {5} = 7 {5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35} b:n kerrannaiset =frac {35} {7} = 5 {7, 14, 21, 28, 35}ab kahdesti a:n kerrannaisina ja b:n kerrannaisina, joten kokonaiskerrat = a + b - 1 (jossagcd
eq 1 kanssaab )phi(ab) = ab - (a + b - 1) , poistamalla kaikki numerotgcd
eq 1 kanssaab phi(ab) = a(b - 1) - (b - 1) phi(ab) = (a - 1) cdot (b - 1) phi(ab) = phi(a) cdot phi(b)
Esimerkkejä:
phi(5 cdot 7) = phi(5) cdot phi(7) = (5 - 1) cdot (7 - 1) = 24 phi(3 cdot 5) = phi(3) cdot phi(5) = (3 - 1) cdot (5 - 1) = 8 phi(3 cdot 7) = phi(3) cdot phi(7) = (3 - 1) cdot (7 - 1) = 12
3) varten alkuluku p ,phi(p ^ k) = p ^ k – p ^ {k – 1}
Todiste :
phi(p^k) = p ^ k - p ^{k - 1} , jossa p on alkulukup ^ k = p ^ k Yhteensä kerrannaisinap = frac {p ^ k} {p} = p ^ {k - 1} Poistamalla nämä kerrannaisuudet kuten niiden kanssagcd
eq 1 p ^ k = 32 2:n kerrannaiset (kuten heidänkingcd
eq 1 ) = 32 / 2 = 16 {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32}phi(p ^ k) = p ^ k - p ^ {k - 1}
Esimerkkejä:
phi(2 ^ 5) = 2 ^ 5 - 2 ^ {5 - 1} = 32 - 16 = 16 phi(5 ^ 3) = 5 ^ 3 - 5 ^ {3 - 1} = 125 - 25 = 100 phi(3 ^ 5) = 3 ^ 5 - 3 ^ {5 - 1} = 243 - 81 = 162
4) varten kaksi numeroa a ja b phi(a cdot b) = phi(a) cdot phi(b) cdot frac {gcd(a, b)} {phi(gcd(a, b))}
Erikoistapaus: gcd(a, b) = 1
phi(a cdot b) = phi(a) cdot phi(b) cdot frac {1} {phi(1)} = phi(a) cdot phi(b)
Esimerkkejä:
Erikoistapaus : gcd(a, b) = 1 , phi(a cdot b) = phi(a) cdot phi(b) phi(2 cdot 9) = phi(2) cdot phi(9) = 1 cdot 6 = 6 phi(8 cdot 9) = phi(8) cdot phi(9) = 4 cdot 6 = 24 phi(5 cdot 6) = phi(5) cdot phi(6) = 4 cdot 2 = 8 gcd(a, b)
eq 1 , phi(a cdot b) = phi(a) cdot phi(b) cdot frac {gcd(a, b)} {phi(gcd(a, b))} phi(4 cdot 6) = phi(4) cdot phi(6) cdot frac {gcd(4, 6)} {phi(gcd(4, 6))} = 2 cdot 2 cdot frac{2}{1} = 2 cdot 2 cdot 2 = 8 phi(4 cdot 8) = phi(4) cdot phi(8) cdot frac {gcd(4, 8)} {phi(gcd(4, 8))} = 2 cdot 4 cdot frac{4}{2} = 2 cdot 4 cdot 2 = 16 phi(6 cdot 8) = phi(6) cdot phi(8) cdot frac {gcd(6, 8)} {phi(gcd(6, 8))} = 2 cdot 4 cdot frac{2}{1} = 2 cdot 4 cdot 2 = 16
5) Kaikkien n:n jakajien kokonaisfunktioiden arvojen summa on yhtä suuri kuin n.
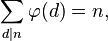
Esimerkkejä:
n = 6
tekijät = {1, 2, 3, 6}
n =phi(1) + phi(2) + phi(3) + phi(6) = 1 + 1 + 2 + 2 = 6phi(1) + phi(2) + phi(4) + phi(8) = 1 + 1 + 2 + 4 = 8phi(1) + phi(2) + phi(5) + phi(10) = 1 + 1 + 4 + 4 = 10
6) Tunnetuin ja tärkein ominaisuus ilmaistaan Eulerin lause :
Lauseen mukaan jos n ja a ovat koprime
(tai suhteellisen ensiluokkaiset) positiiviset kokonaisluvut
aΦ(n)Φ 1 (mod n)
The RSA-salausjärjestelmä perustuu tähän lauseeseen:
Erityisessä tapauksessa, kun m on alkuluku eli p, Eulerin lause muuttuu ns Fermatin pieni lause :
ap-1Φ 1 (p:tä vastaan)
7) Moduulilisäyksen alaisen äärellisen syklisen ryhmän generaattorien lukumäärä on Φ(n) .
Aiheeseen liittyvä artikkeli:
Eulerin Totient-funktio kaikille luvuille, jotka ovat pienempiä tai yhtä suuria kuin n
Optimoitu Euler Totient -funktio useisiin arviointeihin
Viitteet:
http://e-maxx.ru/algo/euler_function
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler%27s_totient_function
https://cp-algorithms.com/algebra/phi-function.html
http://mathcenter.oxford.memory.edu/site/math125/chineseRemainderTheorem/