AVL-puu:
AVL-puu on itsetasapainottava binäärihakupuu ( BST ), jossa vasemman ja oikean alipuun korkeusero ei voi olla suurempi kuin yksi kaikille solmuille.
Esimerkki AVL-puusta:
Yllä oleva puu on AVL, koska jokaisen solmun vasemman ja oikean alipuun korkeuksien erot ovat pienempiä tai yhtä suuria kuin 1.
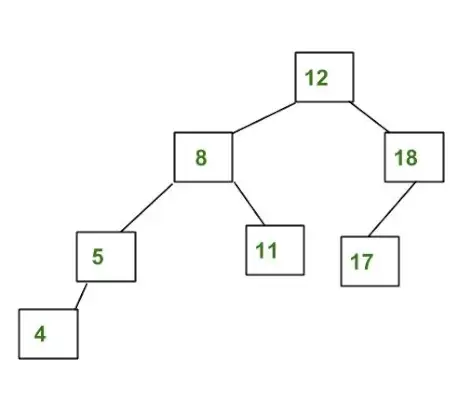
Esimerkki puusta, joka EI ole AVL-puu:

Yllä oleva puu ei ole AVL, koska erot vasemman ja oikean alipuiden välillä 8 ja 12 ovat suurempia kuin 1.
Miksi AVL Trees?
Suurin osa BST-operaatioista (esim. haku, maksimi, min, lisää, poista jne.) kestää Vai niin) aika missä h on BST:n korkeus. Näiden toimintojen kustannukset voivat nousta Päällä) a vinossa binaaripuu . Jos varmistamme, että puun korkeus säilyy O(log(n)) jokaisen lisäyksen ja poiston jälkeen voimme taata ylärajan O(log(n)) kaikkia näitä operaatioita varten. AVL-puun korkeus on aina O(log(n)) missä n on puun solmujen lukumäärä.
Lisäys AVL-puussa:
Varmistaaksemme, että annettu puu pysyy AVL:nä jokaisen lisäyksen jälkeen, meidän on täydennettävä tavallista BST-lisäystoimintoa suorittaaksesi uudelleen tasapainotuksen.
Seuraavassa on kaksi perustoimintoa, jotka voidaan suorittaa BST:n tasapainottamiseksi rikkomatta BST-ominaisuutta (avaimet (vasemmalla)
- Kierto vasemmalle
- Oikea kierto
T1, T2 and T3 are subtrees of the tree, rooted with y (on the left side) or x (on the right side) y x / Right Rotation / x T3 - - - - - - ->T1 ja / <- - - - - - - / T1 T2 Left Rotation T2 T3 Keys in both of the above trees follow the following order keys(T1) < key(x) < keys(T2) < key(y) < keys(T3) So BST property is not violated anywhere.>Suositeltu käytäntö AVL-puun lisääminen Kokeile sitä!
Noudatettavat vaiheet lisäämistä varten:
Olkoon juuri lisätty solmu Sisään
- Suorita standardi BST insert for Sisään .
- Alkaen Sisään , matkusta ylös ja löydä ensimmäinen epätasapainoinen solmu . Antaa Kanssa olla ensimmäinen epätasapainoinen solmu, ja ole lapsi / Kanssa joka tulee polulle Sisään to Kanssa ja x ole lapsenlapsi / Kanssa joka tulee polulle Sisään to Kanssa .
- Tasapainota puu suorittamalla asianmukaiset kierrokset alipuussa, jonka juuret ovat Kanssa. Voi olla 4 mahdollista tapausta, jotka on käsiteltävä x, y ja Kanssa voidaan järjestää 4 tavalla.
- Seuraavassa on 4 mahdollista järjestelyä:
- y on z:n vasen lapsi ja x on y:n vasen lapsi (vasen kirjainkoko)
- y on z:n vasen lapsi ja x on y:n oikea lapsi (vasen oikea kirjainkoko)
- y on z:n oikea lapsi ja x on y:n oikea lapsi (Right Right Case)
- y on z:n oikea lapsi ja x on y:n vasen lapsi (Right Left Case)
Seuraavassa on toiminnot, jotka on suoritettava edellä mainituissa 4 tapauksessa. Kaikissa tapauksissa meidän tarvitsee vain tasapainottaa uudelleen alipuu, jonka juuret ovat Kanssa ja koko puu tasapainottuu, kun alipuun korkeus (asianmukaisten kiertojen jälkeen) juurtuu Kanssa muuttuu samaksi kuin se oli ennen lisäystä.
1. Vasen vasen kotelo
T1, T2, T3 and T4 are subtrees. z y / / y T4 Right Rotate (z) x z / - - - - - - - - ->/ / x T3 T1 T2 T3 T4 / T1 T2>
2. Vasen oikea kotelo
z z x / / / y T4 Left Rotate (y) x T4 Right Rotate(z) y z / - - - - - - - - ->/ - - - - - - - -> / / T1 x y T3 T1 T2 T3 T4 / / T2 T3 T1 T2>
3. Oikea oikea tapaus
z y / / T1 y Left Rotate(z) z x / - - - - - - - ->/ / T2 x T1 T2 T3 T4 / T3 T4>
4. Oikea vasen kotelo
z z x / / / T1 y Right Rotate (y) T1 x Left Rotate(z) z y / - - - - - - - - ->/ - - - - - - - -> / / x T4 T2 y T1 T2 T3 T4 / / T2 T3 T3 T4>
Kuva lisäyksestä AVL-puussa





Lähestyä:
Ajatuksena on käyttää rekursiivista BST-inserttiä, lisäyksen jälkeen saamme osoittimet kaikkiin esivanhempiin yksitellen alhaalta ylöspäin. Emme siis tarvitse vanhempien osoitinta matkustaaksemme ylös. Itse rekursiivinen koodi kulkee ylöspäin ja vierailee äskettäin lisätyn solmun kaikissa esivanhemmissa.
Toteuta idea noudattamalla alla mainittuja vaiheita:
- Suorita normaali BST-lisäys.
- Nykyisen solmun on oltava yksi juuri lisätyn solmun esivanhemmista. Päivitä korkeus nykyisestä solmusta.
- Hanki tasapainotekijä (vasemman alipuun korkeus - oikean alipuun korkeus) nykyisestä solmusta.
- Jos tasapainokerroin on suurempi kuin 1, silloin nykyinen solmu on epätasapainossa ja olemme joko Vasen Vasen kotelo tai vasen Oikea tapaus . Tarkistaaksesi onko se vasen vasen tapaus tai ei, vertaa äskettäin asetettua avainta avaimeen vasen alipuun juuri .
- Jos tasapainokerroin on pienempi kuin -1 , silloin nykyinen solmu on epätasapainossa ja olemme joko oikeassa oikeassa tai oikea-vasemmassa tapauksessa. Tarkistaaksesi, onko kyseessä oikea kirjainkoko vai ei, vertaa juuri lisättyä avainta oikean alipuun juuren avaimeen.
Alla on yllä olevan lähestymistavan toteutus:
C++14
// C++ program to insert a node in AVL tree> #include> using> namespace> std;> > // An AVL tree node> class> Node> {> >public>:> >int> key;> >Node *left;> >Node *right;> >int> height;> };> > // A utility function to get the> // height of the tree> int> height(Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> N->korkeus;>> // A utility function to get maximum> // of two integers> int> max(>int> a,>int> b)> {> >return> (a>b)? a: b;>> /* Helper function that allocates a> >new node with the given key and> >NULL left and right pointers. */> Node* newNode(>int> key)> {> >Node* node =>new> Node();> >node->avain = avain;>> // added at leaf> >return>(node);> }> > // A utility function to right> // rotate subtree rooted with y> // See the diagram given above.> Node *rightRotate(Node *y)> {> >Node *x = y->vasemmalle;>> // Perform rotation> >x->oikea = y;>> // Update heights> >y->korkeus = max(korkeus(y->vasen),> >height(y->oikealla)) + 1;>> >height(x->oikealla)) + 1;>> // Return new root> >return> x;> }> > // A utility function to left> // rotate subtree rooted with x> // See the diagram given above.> Node *leftRotate(Node *x)> {> >Node *y = x->oikea;>> // Perform rotation> >y->vasen = x;>> // Update heights> >x->korkeus = max(korkeus(x->vasen),> >height(x->oikealla)) + 1;>> >height(y->oikealla)) + 1;>> // Return new root> >return> y;> }> > // Get Balance factor of node N> int> getBalance(Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> height(N->vasen) - korkeus(N->oikea);>> // Recursive function to insert a key> // in the subtree rooted with node and> // returns the new root of the subtree.> Node* insert(Node* node,>int> key)> {> >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node == NULL)> >return>(newNode(key));> > >if> (key key)> >node->vasen = insert(solmu->vasen, avain);>> if> (key>solmu->avain)>> // Equal keys are not allowed in BST> >return> node;> > >/* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */> >node->korkeus = 1 + max(korkeus(solmu->vasen),> >height(node->oikealla));>> /* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor> >node to check whether this node became> >unbalanced */> >int> balance = getBalance(node);> > >// If this node becomes unbalanced, then> >// there are 4 cases> > >// Left Left Case> >if> (balance>1 &&-näppäin vasen->näppäin)> >return> rightRotate(node);> > >// Right Right Case> >if> (balance node->oikea->näppäin)>> leftRotate(node);> > >// Left Right Case> >if> (balance>1 &&-näppäin> solmu->vasen->näppäin)> >{> >node->vasen = vasenKierrä(solmu->vasen);>> rightRotate(node);> >}> > >// Right Left Case> >if> (balance <-1 && key right->avain)>> >{> >node->oikea = oikeaKierrä(solmu->oikea);>> leftRotate(node);> >}> > >/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */> >return> node;> }> > // A utility function to print preorder> // traversal of the tree.> // The function also prints height> // of every node> void> preOrder(Node *root)> {> >if>(root != NULL)> >{> >cout ' '; preOrder(root->vasen); preOrder(root->right); } } // Ohjainkoodi int main() { Solmu *root = NULL; /* Yllä olevassa kuvassa annettu rakennuspuu */ root = insert(juuri, 10); juuri = insert(juuri, 20); juuri = insert(juuri, 30); juuri = insert(juuri, 40); juuri = insert(juuri, 50); juuri = insert(juuri, 25); /* Rakennettu AVL-puu olisi 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ cout<< 'Preorder traversal of the ' 'constructed AVL tree is
'; preOrder(root); return 0; } // This code is contributed by // rathbhupendra> |
>
>
C
// C program to insert a node in AVL tree> #include> #include> > // An AVL tree node> struct> Node> {> >int> key;> >struct> Node *left;> >struct> Node *right;> >int> height;> };> > // A utility function to get the height of the tree> int> height(>struct> Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> N->korkeus;>> // A utility function to get maximum of two integers> int> max(>int> a,>int> b)> {> >return> (a>b)? a: b;>> /* Helper function that allocates a new node with the given key and> >NULL left and right pointers. */> struct> Node* newNode(>int> key)> {> >struct> Node* node = (>struct> Node*)> >malloc>(>sizeof>(>struct> Node));> >node->avain = avain;>> return>(node);> }> > // A utility function to right rotate subtree rooted with y> // See the diagram given above.> struct> Node *rightRotate(>struct> Node *y)> {> >struct> Node *x = y->vasemmalle;>> Node *T2 = x->oikea;>> // Perform rotation> >x->oikea = y;>> // Update heights> >y->korkeus = max(korkeus(y->vasen),> >height(y->oikealla)) + 1;>> >height(x->oikealla)) + 1;>> // Return new root> >return> x;> }> > // A utility function to left rotate subtree rooted with x> // See the diagram given above.> struct> Node *leftRotate(>struct> Node *x)> {> >struct> Node *y = x->oikea;>> Node *T2 = y->vasemmalle;>> // Perform rotation> >y->vasen = x;>> // Update heights> >x->korkeus = max(korkeus(x->vasen),> >height(x->oikealla)) + 1;>> >height(y->oikealla)) + 1;>> // Return new root> >return> y;> }> > // Get Balance factor of node N> int> getBalance(>struct> Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> height(N->vasen) - korkeus(N->oikea);>> // Recursive function to insert a key in the subtree rooted> // with node and returns the new root of the subtree.> struct> Node* insert(>struct> Node* node,>int> key)> {> >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node == NULL)> >return>(newNode(key));> > >if> (key key)> >node->vasen = insert(solmu->vasen, avain);>> if> (key>solmu->avain)>> // Equal keys are not allowed in BST> >return> node;> > >/* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */> >node->korkeus = 1 + max(korkeus(solmu->vasen),> >height(node->oikealla));>> /* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor> >node to check whether this node became> >unbalanced */> >int> balance = getBalance(node);> > >// If this node becomes unbalanced, then> >// there are 4 cases> > >// Left Left Case> >if> (balance>1 &&-näppäin vasen->näppäin)> >return> rightRotate(node);> > >// Right Right Case> >if> (balance node->oikea->näppäin)>> leftRotate(node);> > >// Left Right Case> >if> (balance>1 &&-näppäin> solmu->vasen->näppäin)> >{> >node->vasen = vasenKierrä(solmu->vasen);>> rightRotate(node);> >}> > >// Right Left Case> >if> (balance <-1 && key right->avain)>> >{> >node->oikea = oikeaKierrä(solmu->oikea);>> leftRotate(node);> >}> > >/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */> >return> node;> }> > // A utility function to print preorder traversal> // of the tree.> // The function also prints height of every node> void> preOrder(>struct> Node *root)> {> >if>(root != NULL)> >{> >printf>(>'%d '>, root->avain);>> }> > /* Driver program to test above function*/> int> main()> {> >struct> Node *root = NULL;> > >/* Constructing tree given in the above figure */> >root = insert(root, 10);> >root = insert(root, 20);> >root = insert(root, 30);> >root = insert(root, 40);> >root = insert(root, 50);> >root = insert(root, 25);> > >/* The constructed AVL Tree would be> >30> >/> >20 40> >/> >10 25 50> >*/> > >printf>(>'Preorder traversal of the constructed AVL'> >' tree is
'>);> >preOrder(root);> > >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
Java
// Java program for insertion in AVL Tree> class> Node {> >int> key, height;> >Node left, right;> > >Node(>int> d) {> >key = d;> >height =>1>;> >}> }> > class> AVLTree {> > >Node root;> > >// A utility function to get the height of the tree> >int> height(Node N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0>;> > >return> N.height;> >}> > >// A utility function to get maximum of two integers> >int> max(>int> a,>int> b) {> >return> (a>b)? a: b;>> > >// A utility function to right rotate subtree rooted with y> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node rightRotate(Node y) {> >Node x = y.left;> >Node T2 = x.right;> > >// Perform rotation> >x.right = y;> >y.left = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) +>1>;> >x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) +>1>;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> >}> > >// A utility function to left rotate subtree rooted with x> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node leftRotate(Node x) {> >Node y = x.right;> >Node T2 = y.left;> > >// Perform rotation> >y.left = x;> >x.right = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) +>1>;> >y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) +>1>;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> >}> > >// Get Balance factor of node N> >int> getBalance(Node N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0>;> > >return> height(N.left) - height(N.right);> >}> > >Node insert(Node node,>int> key) {> > >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return> (>new> Node(key));> > >if> (key node.left = insert(node.left, key); else if (key>solmu.avain) solmu.oikea = insert(solmu.oikea, avain); else // Päällekkäisiä avaimia ei sallita palauttaa solmu; /* 2. Päivitä tämän esi-isolmun korkeus */ solmu.korkeus = 1 + max(korkeus(solmu.vasen), korkeus(solmu.oikea)); /* 3. Hanki tämän esisolmun tasapainokerroin tarkistaaksesi, onko tämä solmu epätasapainossa */ int balance = getBalance(node); // Jos tämä solmu tulee epätasapainoiseksi, // on 4 tapausta Left Left Case if (saldo> 1 && avain return rightRotate(node); // Oikea Oikea Case if (balance<-1 && key>solmu.oikea.avain) return leftRotate(node); // Vasen Oikea Kirjainkoko if (tasapaino> 1 && avain> solmu.vasen.avain) { solmu.vasen = vasenKierrä(solmu.vasen); paluu oikealleKierrä(solmu); } // Oikea Vasen Kirjainkoko if (tasapaino<-1 && key node.right = rightRotate(node.right); return leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node void preOrder(Node node) { if (node != null) { System.out.print(node.key + ' '); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } public static void main(String[] args) { AVLTree tree = new AVLTree(); /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ System.out.println('Preorder traversal' + ' of constructed tree is : '); tree.preOrder(tree.root); } } // This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal> |
>
>
Python 3
# Python code to insert a node in AVL tree> > # Generic tree node class> class> TreeNode(>object>):> >def> __init__(>self>, val):> >self>.val>=> val> >self>.left>=> None> >self>.right>=> None> >self>.height>=> 1> > # AVL tree class which supports the> # Insert operation> class> AVL_Tree(>object>):> > ># Recursive function to insert key in> ># subtree rooted with node and returns> ># new root of subtree.> >def> insert(>self>, root, key):> > ># Step 1 - Perform normal BST> >if> not> root:> >return> TreeNode(key)> >elif> key root.left = self.insert(root.left, key) else: root.right = self.insert(root.right, key) # Step 2 - Update the height of the # ancestor node root.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(root.left), self.getHeight(root.right)) # Step 3 - Get the balance factor balance = self.getBalance(root) # Step 4 - If the node is unbalanced, # then try out the 4 cases # Case 1 - Left Left if balance>1 ja avain palauttavat self.rightRotate(root) # Tapaus 2 - Oikea Oikea, jos tasapaino<-1 and key>root.right.val: return self.leftRotate(root) # Tapaus 3 - Vasen Oikea, jos tasapaino> 1 ja avain> root.left.val: root.left = self.leftRotate(root.left) return self.rightRotate(root ) # Tapaus 4 - Oikea Vasen, jos tasapaino<-1 and key root.right = self.rightRotate(root.right) return self.leftRotate(root) return root def leftRotate(self, z): y = z.right T2 = y.left # Perform rotation y.left = z z.right = T2 # Update heights z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left), self.getHeight(z.right)) y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left), self.getHeight(y.right)) # Return the new root return y def rightRotate(self, z): y = z.left T3 = y.right # Perform rotation y.right = z z.left = T3 # Update heights z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left), self.getHeight(z.right)) y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left), self.getHeight(y.right)) # Return the new root return y def getHeight(self, root): if not root: return 0 return root.height def getBalance(self, root): if not root: return 0 return self.getHeight(root.left) - self.getHeight(root.right) def preOrder(self, root): if not root: return print('{0} '.format(root.val), end='') self.preOrder(root.left) self.preOrder(root.right) # Driver program to test above function myTree = AVL_Tree() root = None root = myTree.insert(root, 10) root = myTree.insert(root, 20) root = myTree.insert(root, 30) root = myTree.insert(root, 40) root = myTree.insert(root, 50) root = myTree.insert(root, 25) '''The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50''' # Preorder Traversal print('Preorder traversal of the', 'constructed AVL tree is') myTree.preOrder(root) print() # This code is contributed by Ajitesh Pathak> |
>
>
C#
// C# program for insertion in AVL Tree> using> System;> > class> Node> {> >public> int> key, height;> >public> Node left, right;> > >public> Node(>int> d)> >{> >key = d;> >height = 1;> >}> }> > public> class> AVLTree> {> > >Node root;> > >// A utility function to get> >// the height of the tree> >int> height(Node N)> >{> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0;> > >return> N.height;> >}> > >// A utility function to get> >// maximum of two integers> >int> max(>int> a,>int> b)> >{> >return> (a>b)? a: b;>> > >// A utility function to right> >// rotate subtree rooted with y> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node rightRotate(Node y)> >{> >Node x = y.left;> >Node T2 = x.right;> > >// Perform rotation> >x.right = y;> >y.left = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y.height = max(height(y.left),> >height(y.right)) + 1;> >x.height = max(height(x.left),> >height(x.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> >}> > >// A utility function to left> >// rotate subtree rooted with x> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node leftRotate(Node x)> >{> >Node y = x.right;> >Node T2 = y.left;> > >// Perform rotation> >y.left = x;> >x.right = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x.height = max(height(x.left),> >height(x.right)) + 1;> >y.height = max(height(y.left),> >height(y.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> >}> > >// Get Balance factor of node N> >int> getBalance(Node N)> >{> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0;> > >return> height(N.left) - height(N.right);> >}> > >Node insert(Node node,>int> key)> >{> > >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return> (>new> Node(key));> > >if> (key node.left = insert(node.left, key); else if (key>solmu.avain) solmu.oikea = insert(solmu.oikea, avain); else // Päällekkäisiä avaimia ei sallita palauttaa solmu; /* 2. Päivitä tämän esi-isolmun korkeus */ solmu.korkeus = 1 + max(korkeus(solmu.vasen), korkeus(solmu.oikea)); /* 3. Hanki tämän esisolmun tasapainokerroin tarkistaaksesi, onko tämä solmu epätasapainossa */ int balance = getBalance(node); // Jos tämä solmu tulee epätasapainoiseksi, // on 4 tapausta Left Left Case if (tasapaino> 1 && avain return rightRotate(node); // Oikea Oikea Case if (balance node.right.key) return leftRotate(node) ; // Vasen oikea kirjainkoko if (tasapaino> 1 && avain> solmu.vasen.avain) { solmu.vasen = leftRotate(solmu.vasen) // Oikea kirjainkoko if (tasapaino);<-1 && key < node.right.key) { node.right = rightRotate(node.right); return leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node void preOrder(Node node) { if (node != null) { Console.Write(node.key + ' '); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } // Driver code public static void Main(String[] args) { AVLTree tree = new AVLTree(); /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ Console.Write('Preorder traversal' + ' of constructed tree is : '); tree.preOrder(tree.root); } } // This code has been contributed // by PrinciRaj1992> |
>
>
Javascript
> > >// JavaScript program for insertion in AVL Tree> >class Node {> >constructor(d) {> >this>.key = d;> >this>.height = 1;> >this>.left =>null>;> >this>.right =>null>;> >}> >}> > >class AVLTree {> >constructor() {> >this>.root =>null>;> >}> > >// A utility function to get> >// the height of the tree> >height(N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)>return> 0;> > >return> N.height;> >}> > >// A utility function to get> >// maximum of two integers> >max(a, b) {> >return> a>b ? a: b;>> > >// A utility function to right> >// rotate subtree rooted with y> >// See the diagram given above.> >rightRotate(y) {> >var> x = y.left;> >var> T2 = x.right;> > >// Perform rotation> >x.right = y;> >y.left = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(y.left),> >this>.height(y.right)) + 1;> >x.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(x.left),> >this>.height(x.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> >}> > >// A utility function to left> >// rotate subtree rooted with x> >// See the diagram given above.> >leftRotate(x) {> >var> y = x.right;> >var> T2 = y.left;> > >// Perform rotation> >y.left = x;> >x.right = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(x.left),> >this>.height(x.right)) + 1;> >y.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(y.left),> >this>.height(y.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> >}> > >// Get Balance factor of node N> >getBalance(N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)>return> 0;> > >return> this>.height(N.left) ->this>.height(N.right);> >}> > >insert(node, key) {> >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node ==>null>)>return> new> Node(key);> > >if> (key node.left = this.insert(node.left, key); else if (key>solmu.avain) solmu.oikea = this.insert(solmu.oikea, avain); // Päällekkäisiä avaimia ei sallita muuten palauttaa solmun; /* 2. Päivitä tämän esi-isolmun korkeus */ solmu.korkeus = 1 + this.max(this.height(solmu.vasen), this.height(solmu.oikea)); /* 3. Hanki tämän esisolmun tasapainokerroin tarkistaaksesi, onko tämä solmu epätasapainossa */ var balance = this.getBalance(node); // Jos tämä solmu tulee epätasapainoiseksi, // on 4 tapausta Left Left Case if (balance> 1 && key return this.rightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (balance node.right.key) palauttaa tämän. leftRotate(node); // Vasen Oikea Kirjainkoko if (tasapaino> 1 && avain> solmu.vasen.avain) { solmu.vasen = this.leftRotate(node.left) return this.right(node); Vasen kirjainkoko jos (saldo<-1 && key < node.right.key) { node.right = this.rightRotate(node.right); return this.leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node preOrder(node) { if (node != null) { document.write(node.key + ' '); this.preOrder(node.left); this.preOrder(node.right); } } } // Driver code var tree = new AVLTree(); /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ document.write( 'Preorder traversal of the ' + 'constructed AVL tree is ' ); tree.preOrder(tree.root);> |
>
>Lähtö
Preorder traversal of the constructed AVL tree is 30 20 10 25 40 50>
Monimutkaisuusanalyysi
Aika monimutkaisuus: O(log(n)), lisättäväksi
Aputila: O(1)
merkkijonojen rakentaja java
Kiertotoiminnot (kierto vasemmalle ja oikealle) vievät jatkuvasti aikaa, koska siellä vaihdetaan vain muutamia osoittimia. Korkeuden päivittäminen ja tasapainokertoimen saaminen vie myös jatkuvasti aikaa. Joten AVL-insertin aikamonimutkaisuus pysyy samana kuin BST-lisäyksen, joka on O(h), missä h on puun korkeus. Koska AVL-puu on tasapainotettu, korkeus on O(Logn). Joten AVL-insertin aikamonimutkaisuus on O(Logn).
Vertailu Red Black Treeen:
AVL-puu ja muut itsetasapainottavat hakupuut, kuten Red Black, ovat hyödyllisiä kaikkien perustoimintojen suorittamiseen O(log n) ajassa. AVL-puut ovat tasapainoisempia kuin puna-mustat puut, mutta ne voivat aiheuttaa enemmän kiertoja lisäyksen ja poistamisen aikana. Joten jos sovelluksesi sisältää monia toistuvia lisäyksiä ja poistoja, kannattaa suosia Red Black -puita. Ja jos lisäykset ja poistot ovat harvempia ja haku on useammin käytetty toimenpide, niin AVL-puuta tulisi suosia Red Black Tree:n sijaan.
Seuraava on viesti poistettavaksi AVL-puussa:
AVL-puu | Sarja 2 (poisto)
