Annettu suorakaiteen muotoinen paperi, jonka mitat a x b . Tehtävänä on leikata koko paperi minimi määrä neliö kappaletta. Voimme valita minkä tahansa kokoisia neliömäisiä kappaleita, mutta ne on leikattava menemättä päällekkäin tai jättämättä ylimääräistä tilaa .
Esimerkkejä:
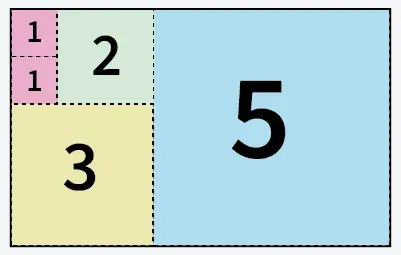
Syöte: a = 5 b = 8
5 ruutua leikattu paperista, jonka koko on 5 x 8
Lähtö: 5
Selitys: Voimme leikata paperin 5 ruutuun: 1 neliö, jonka koko on 5x5, 1 neliö, jonka koko on 3x3, 1 neliö, jonka koko on 2x2 ja 2 neliötä, joiden koko on 1x1.Syöte: a = 13 b = 11
6 ruutua leikattu paperista, jonka koko on 13 x 11
Lähtö: 6
Selitys: Voimme leikata paperin 6 ruutuun: 1 neliö, jonka koko on 7x7, 1 neliö, jonka koko on 6x6, 1 neliö, jonka koko on 5x5, 2 neliötä, jonka koko on 4x4 ja 1 neliö, jonka koko on 1x1.shreya ghoshal ensimmäinen aviomiesSyöte: a = 6 b = 7
5 ruutua leikattu paperista, jonka koko on 6 x 7
Lähtö: 5
Selitys: Voimme leikata paperin 5 ruutuun: 1 neliö kooltaan 4x4 2 ruutua kokoa 3x3 ja 2 ruutua kokoa 3x3.
Sisällysluettelo
- [Väärä lähestymistapa 1] Ahneella tekniikalla
- [Väärä lähestymistapa 2] Dynaamisen ohjelmoinnin käyttäminen
- [Oikea lähestymistapa] DFS:n ja dynaamisen ohjelmoinnin käyttäminen
[Väärä lähestymistapa 1] Ahneella tekniikalla
Ensi näkemältä saattaa vaikuttaa siltä, että ongelma voidaan ratkaista helposti leikkaamalla paperista ensin suurin mahdollinen neliö, minkä jälkeen leikkaamalla jäljellä olevasta paperista suurin neliö ja niin edelleen, kunnes olemme leikaneet koko paperin. Mutta tämä ratkaisu on väärä.
Miksi Greedy Approach ei toimi?
Harkitse kokoista paperia 6x7 sitten jos yritämme leikata paperia ahneesti, saamme sen 7 neliöt: 1 neliön kokoinen 6x6 ja 6 neliötä 1x1 kun taas oikea ratkaisu on: 5. Näin ollen ahne lähestymistapa ei toimi.
[Väärä lähestymistapa 2] Dynaamisen ohjelmoinnin käyttäminen
Dynaaminen ohjelmointi pysty- tai vaakasuuntaisilla leikkauksilla: Toinen ratkaisu, joka saattaa vaikuttaa oikealta, on käyttää Dynaaminen ohjelmointi . Voimme ylläpitää dp[][]-taulukkoa siten, että dp[i][j] = pienin määrä neliöitä, jotka voidaan leikata kokoisesta paperista i x j . Sitten kokoiselle paperille axb
- Voimme yrittää leikata sen jokaista riviä pitkin: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i - k][j] + dp[k][j]) missä k voi olla alueella [1 i - 1].
- Voimme yrittää leikata sen jokaista saraketta pitkin: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i][j - k] + dp[i][k]) missä k voi olla alueella [1 j - 1].
Lopulta kaikkien leikkausten vähimmäismäärä on vastaus. Mutta tämä ratkaisu on myös väärä.
pinoa javassaMiksi pysty- tai vaakasuuntainen leikkaaminen dynaamisella ohjelmointimenetelmällä ei toimi?
Tämä ei toimi, koska oletamme, että pysty- tai vaakasuora leikkaus jakaa aina suorakulmion kahteen osaan. Harkitse kokoista paperia 13x11 sitten jos yritämme leikata paperia DP-lähestymistavalla, saamme 8 ruutua, mutta oikea vastaus (kuten esimerkeissä) on 6. Näin ollen dynaaminen ohjelmointi ei toimi.
[Oikea lähestymistapa] DFS:n ja dynaamisen ohjelmoinnin käyttäminen
C++The idea on leikata koko paperi käyttämällä DFS sisään alhaalta ylöspäin tavalla. Etsi joka vaiheessa paperin alin vasen kulma ja yritä leikata siitä kulmasta kaikenkokoisia neliöitä. Kun olet leikannut neliön uudelleen, etsi jäljellä olevan paperin vasen alin kulma ja leikkaa kaikki mahdolliset neliöt ja niin edelleen. Mutta jos kokeilemme kaikkia mahdollisia leikkauksia jokaisen mahdollisen paperikoon vasemmasta alimmasta kulmasta, se olisi melko tehotonta. Voimme optimoida sen käyttämällä Dynaaminen ohjelmointi tallentaaksesi vähimmäisleikkaukset jokaiselle mahdolliselle paperikoolle.
Minkä tahansa paperikoon yksilöimiseksi voimme ylläpitää remSq[]-taulukkoa siten, että remSq[i] tallentaa jäljellä olevien neliöiden lukumäärän, joiden koko on 1x1, paperin i:nteen sarakkeeseen. Joten paperille, jonka koko on 6x7 remSq[] = {6 6 6 6 6 6 6}. Myös alimman vasemman kulman löytämiseksi löydämme ensimmäisen indeksin, jossa on suurimmat jäljellä olevat neliöt. Joten voimme tiivistää remSq[]-taulukon arvon löytääksemme ainutlaatuisen avaimen kaikille remSq[]-taulukon mahdollisille arvoille.
// C++ Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb #include
// Java Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb import java.util.*; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int base = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Map<Integer Integer> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.containsKey(key)) return memo.get(key); int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = Arrays.copyOf(remSq b); int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo.put(key ans); return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; Arrays.fill(remSq a); Map<Integer Integer> memo = new HashMap<>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Sample Input int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb System.out.println(minCut(a b)); } }
# Python Program to find minimum number of squares to cut # from a paper of size axb # function to get the hash key for remSq array def getKey(remSq b): base = 1 key = 0 for i in range(b): key += remSq[i] * base base = base * (b + 1) return key # Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts # for a given remSq array def minCutUtil(remSq a b memo): # pointers to mark the start and end of range # with maximum remaining squares start = 0 # Check if we have previously calculated the answer # for the same state key = getKey(remSq b) if key in memo: return memo[key] maxRemSq = 0 # Find the starting point of min height for i in range(b): if remSq[i] > maxRemSq: maxRemSq = remSq[i] start = i # If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already # cut the entire paper if maxRemSq == 0: return 0 end = start newRemSq = remSq[:] ans = float('inf') # Find the ending point of min height while end < b: # length of edge of square from start till current end squareEdge = end - start + 1 # If the current column does not have maximum remaining # squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of # size squareEdge then break out of the loop if newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq or newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0: break # If we can cut a square of size squareEdge # update the remainingSquares for i in range(start end + 1): newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge # Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)) end += 1 memo[key] = ans return ans # Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut # using paper of size a X b def minCut(a b): # if the given rectangle is a square if a == b: return 1 # Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns remSq = [a] * b memo = {} return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) if __name__ == '__main__': # Sample Input a = 13 b = 11 # Function call to get minimum number # of squares for axb print(minCut(a b))
// C# Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int baseVal = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * baseVal); baseVal = baseVal * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Dictionary<int int> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.ContainsKey(key)) return memo[key]; int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = (int[])remSq.Clone(); int ans = int.MaxValue; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.Min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) remSq[i] = a; Dictionary<int int> memo = new Dictionary<int int>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } static void Main() { int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb Console.WriteLine(minCut(a b)); } }
// JavaScript Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb // function to get the hash key for remSq array function getKey(remSq b) { let base = 1; let key = 0; for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array function minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares let start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state let key = getKey(remSq b); if (key in memo) return memo[key]; let maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq === 0) return 0; end = start; let newRemSq = remSq.slice(); let ans = Infinity; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end let squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] !== maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (let i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b function minCut(a b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a === b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns let remSq = new Array(b).fill(a); let memo = {}; return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } // Driver Code let a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb console.log(minCut(a b));
Lähtö
6
Aika monimutkaisuus: O(a^b) jokaiselle b sarakkeelle voi olla neliö.
Aputila: O(a^b) koska muistiinpano tallentaa jokaisen yksilöllisen tilan.

 5 ruutua leikattu paperista, jonka koko on 5 x 8
5 ruutua leikattu paperista, jonka koko on 5 x 8 6 ruutua leikattu paperista, jonka koko on 13 x 11
6 ruutua leikattu paperista, jonka koko on 13 x 11 5 ruutua leikattu paperista, jonka koko on 6 x 7
5 ruutua leikattu paperista, jonka koko on 6 x 7